The Importance of Large-Scale Genomic Studies to Unravel Genetic Risk Factors for Autism
- PMID: 38892002
- PMCID: PMC11172008
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115816
The Importance of Large-Scale Genomic Studies to Unravel Genetic Risk Factors for Autism
Abstract
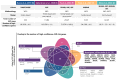
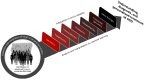
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a common and highly heritable neurodevelopmental disorder. During the last 15 years, advances in genomic technologies and the availability of increasingly large patient cohorts have greatly expanded our knowledge of the genetic architecture of ASD and its neurobiological mechanisms. Over two hundred risk regions and genes carrying rare de novo and transmitted high-impact variants have been identified. Additionally, common variants with small individual effect size are also important, and a number of loci are now being uncovered. At the same time, these new insights have highlighted ongoing challenges. In this perspective article, we summarize developments in ASD genetic research and address the enormous impact of large-scale genomic initiatives on ASD gene discovery.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder; gene discovery; genetic heterogeneity; genomic technologies; large patient cohorts; locus discovery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Maenner M.J., Warren Z., Williams A.R., Amoakohene E., Bakian A.V., Bilder D.A., Durkin M.S., Fitzgerald R.T., Furnier S.M., Hughes M.M., et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder among Children Aged 8 Years-Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2020. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2023;72:1–14. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7202a1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

