The Relationship between Circadian Rhythm and Cancer Disease
- PMID: 38892035
- PMCID: PMC11172077
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115846
The Relationship between Circadian Rhythm and Cancer Disease
Abstract
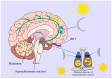
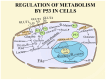
The circadian clock regulates biological cycles across species and is crucial for physiological activities and biochemical reactions, including cancer onset and development. The interplay between the circadian rhythm and cancer involves regulating cell division, DNA repair, immune function, hormonal balance, and the potential for chronotherapy. This highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy circadian rhythm for cancer prevention and treatment. This article investigates the complex relationship between the circadian rhythm and cancer, exploring how disruptions to the internal clock may contribute to tumorigenesis and influence cancer progression. Numerous databases are utilized to conduct searches for articles, such as NCBI, MEDLINE, and Scopus. The keywords used throughout the academic archives are "circadian rhythm", "cancer", and "circadian clock". Maintaining a healthy circadian cycle involves prioritizing healthy sleep habits and minimizing disruptions, such as consistent sleep schedules, reduced artificial light exposure, and meal timing adjustments. Dysregulation of the circadian clock gene and cell cycle can cause tumor growth, leading to the need to regulate the circadian cycle for better treatment outcomes. The circadian clock components significantly impact cellular responses to DNA damage, influencing cancer development. Understanding the circadian rhythm's role in tumor diseases and their therapeutic targets is essential for treating and preventing cancer. Disruptions to the circadian rhythm can promote abnormal cell development and tumor metastasis, potentially due to immune system imbalances and hormonal fluctuations.
Keywords: cancer; circadian rhythm; melatonin; suprachiasmatic nucleus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Moving to the Rhythm with Clock (Circadian) Genes, Autophagy, mTOR, and SIRT1 in Degenerative Disease and Cancer.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2017;14(3):299-304. doi: 10.2174/1567202614666170718092010. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2017. PMID: 28721811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian rhythm disruption and endocrine-related tumors.World J Clin Oncol. 2024 Jul 24;15(7):818-834. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i7.818. World J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39071458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian Clock, Cell Division, and Cancer: From Molecules to Organism.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Apr 20;18(4):873. doi: 10.3390/ijms18040873. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28425940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian molecular clocks and cancer.Cancer Lett. 2014 Jan 1;342(1):9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.09.040. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 24099911 Review.
-
Circadian rhythm disruption in cancer biology.Mol Med. 2012 Dec 6;18(1):1249-60. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2012.00077. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22811066 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circadian syndrome and mortality risk in adults aged ≥ 40 years: a prospective cohort analysis of CHARLS and NHANES.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 28;15(1):14791. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99631-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40295832 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the link between circadian clock genes and brain tumors: From pathological disruptions to potential therapeutic interventions.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 27;16:1617713. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1617713. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40495887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The immunomodulatory effects of vitamins in cancer.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 7;15:1464329. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1464329. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39434876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep Traits to the Risk of Breast Cancer Disease Incidence, Adverse Progression and Mortality: Evidence From a Global Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Public Health. 2025 Jul 15;70:1608535. doi: 10.3389/ijph.2025.1608535. eCollection 2025. Int J Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40735026 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of scRNA-Seq and Bulk RNA-Seq Identifies Circadian Rhythm Disruption-Related Genes Associated with Prognosis and Drug Resistance in Colorectal Cancer Patients.Immunotargets Ther. 2025 Apr 11;14:475-489. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S499806. eCollection 2025. Immunotargets Ther. 2025. PMID: 40241740 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

