Arabidopsis Transcriptomics Reveals the Role of Lipoxygenase2 (AtLOX2) in Wound-Induced Responses
- PMID: 38892085
- PMCID: PMC11173247
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115898
Arabidopsis Transcriptomics Reveals the Role of Lipoxygenase2 (AtLOX2) in Wound-Induced Responses
Abstract
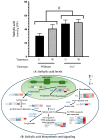
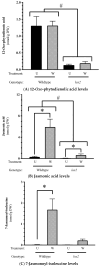
In wounded Arabidopsis thaliana leaves, four 13S-lipoxygenases (AtLOX2, AtLOX3, AtLOX4, AtLOX6) act in a hierarchical manner to contribute to the jasmonate burst. This leads to defense responses with LOX2 playing an important role in plant resistance against caterpillar herb-ivory. In this study, we sought to characterize the impact of AtLOX2 on wound-induced phytohormonal and transcriptional responses to foliar mechanical damage using wildtype (WT) and lox2 mutant plants. Compared with WT, the lox2 mutant had higher constitutive levels of the phytohormone salicylic acid (SA) and enhanced expression of SA-responsive genes. This suggests that AtLOX2 may be involved in the biosynthesis of jasmonates that are involved in the antagonism of SA biosynthesis. As expected, the jasmonate burst in response to wounding was dampened in lox2 plants. Generally, 1 h after wounding, genes linked to jasmonate biosynthesis, jasmonate signaling attenuation and abscisic acid-responsive genes, which are primarily involved in wound sealing and healing, were differentially regulated between WT and lox2 mutants. Twelve h after wounding, WT plants showed stronger expression of genes associated with plant protection against insect herbivory. This study highlights the dynamic nature of jasmonate-responsive gene expression and the contribution of AtLOX2 to this pathway and plant resistance against insects.
Keywords: 13S-lipoxygenase; AtLOX2; jasmonate; transcriptome; wounding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures










References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

