Melatonin-Regulated Chaperone Binding Protein Plays a Key Role in Cadmium Stress Tolerance in Rice, Revealed by the Functional Characterization of a Novel Serotonin N-Acetyltransferase 3 (SNAT3) in Rice
- PMID: 38892140
- PMCID: PMC11172786
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115952
Melatonin-Regulated Chaperone Binding Protein Plays a Key Role in Cadmium Stress Tolerance in Rice, Revealed by the Functional Characterization of a Novel Serotonin N-Acetyltransferase 3 (SNAT3) in Rice
Abstract
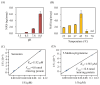
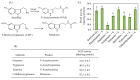
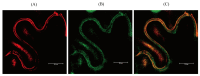
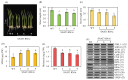
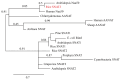
The study of the mechanisms by which melatonin protects against cadmium (Cd) toxicity in plants is still in its infancy, particularly at the molecular level. In this study, the gene encoding a novel serotonin N-acetyltransferase 3 (SNAT3) in rice, a pivotal enzyme in the melatonin biosynthetic pathway, was cloned. Rice (Oryza sativa) OsSNAT3 is the first identified plant ortholog of archaeon Thermoplasma volcanium SNAT. The purified recombinant OsSNAT3 catalyzed the conversion of serotonin and 5-methoxytryptamine to N-acetylserotonin and melatonin, respectively. The suppression of OsSNAT3 by RNAi led to a decline in endogenous melatonin levels followed by a reduction in Cd tolerance in transgenic RNAi rice lines. In addition, the expression levels of genes encoding the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperones BiP3, BiP4, and BiP5 were much lower in RNAi lines than in the wild type. In transgenic rice plants overexpressing OsSNAT3 (SNAT3-OE), however, melatonin levels were higher than in wild-type plants. SNAT3-OE plants also tolerated Cd stress, as indicated by seedling growth, malondialdehyde, and chlorophyll levels. BiP4 expression was much higher in the SNAT3-OE lines than in the wild type. These results indicate that melatonin engineering could help crops withstand Cd stress, resulting in high yields in Cd-contaminated fields.
Keywords: binding proteins; cadmium tolerance; chaperone; melatonin; serotonin N-acetyltransferase; transgenic rice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Saqib M., Shahzad U., Zulfiqar F., Tiwari R.K., Lal M.K., Naz S., Jahan M.S., Awan Z.A., El-Sheikh M.A., Altaf M.A. Exogenous melatonin alleviates cadmium-induced inhibition of growth and photosynthesis through upregulating antioxidant defense system in strawberry. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023;157:10–18. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2023.03.039. - DOI
-
- Zulfiqar U., Jiang W., Xiukang W., Hussain S., Ahmad M., Maqsood M.F., Ali N., Ishfaq M., Kaleem M., Haider U., et al. Cadmium phytotoxicity, tolerance, and advanced remediation approaches in agricultural soils; a comprehensive review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022;13:773815. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.773815. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

