Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Tezepelumab in Airway Diseases: From Physiological Role to Target Therapy
- PMID: 38892164
- PMCID: PMC11172531
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115972
Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Tezepelumab in Airway Diseases: From Physiological Role to Target Therapy
Abstract
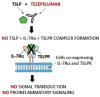
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), is a protein belonging to a class of epithelial cytokines commonly called alarmins, which also includes IL-25 and IL-33. Functionally, TSLP is a key player in the immune response to environmental insults, initiating a number of downstream inflammatory pathways. TSLP performs its role by binding to a high-affinity heteromeric complex composed of the thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor (TSLPR) chain and IL-7Rα. In recent years, the important role of proinflammatory cytokines in the etiopathogenesis of various chronic diseases such as asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP), chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPDs), and chronic spontaneous urticaria has been studied. Although alarmins have been found to be mainly implicated in the mechanisms of type 2 inflammation, studies on monoclonal antibodies against TSLP demonstrate partial efficacy even in patients whose inflammation is not definable as T2 and the so-called low T2. Tezepelumab is a human anti-TSLP antibody that prevents TSLP-TSLPR interactions. Several clinical trials are evaluating the safety and efficacy of Tezepelumab in various inflammatory disorders. In this review, we will highlight major recent advances in understanding the functional role of TSLP, its involvement in Th2-related diseases, and its suitability as a target for biological therapies.
Keywords: CRSwNP; T2 inflammation; TSLP; Tezepelumab; alarmins; cytokines; epithelium; mechanisms; severe asthma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP): Evidence in Respiratory Epithelial-driven Diseases Including Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024 Dec 5;25(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s11882-024-01186-2. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024. PMID: 39636450 Review.
-
Expression and Regulation of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Receptor Heterocomplex in the Innate-Adaptive Immunity of Pediatric Asthma.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 18;19(4):1231. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041231. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29670037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tezepelumab: a novel biological therapy for the treatment of severe uncontrolled asthma.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2019 Nov;28(11):931-940. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2019.1672657. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31549891 Review.
-
Tezepelumab: an anti-thymic stromal lymphopoietin monoclonal antibody for the treatment of asthma.Immunotherapy. 2023 Dec;15(17):1435-1447. doi: 10.2217/imt-2023-0079. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Immunotherapy. 2023. PMID: 37724378 Review.
-
Anti-TSLP antibodies: Targeting a master regulator of type 2 immune responses.Allergol Int. 2020 Apr;69(2):197-203. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2020.01.001. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Allergol Int. 2020. PMID: 31974038 Review.
Cited by
-
TSLP and TSLPR Expression Levels in Peripheral Blood as Potential Biomarkers in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 30;26(3):1227. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031227. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940994 Free PMC article.
-
[Diagnosis and drug therapy of chronic rhinosinusitis].HNO. 2025 Jul;73(7):441-460. doi: 10.1007/s00106-025-01635-y. Epub 2025 Apr 16. HNO. 2025. PMID: 40237828 Free PMC article. German.
-
Update on the genetics of allergic diseases.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025 Jun;155(6):1738-1752. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2025.03.012. Epub 2025 Mar 24. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40139464 Review.
-
Dupilumab Effectiveness in Patients with Severe Allergic Asthma Non-Responsive to Omalizumab.J Pers Med. 2025 Jan 23;15(2):43. doi: 10.3390/jpm15020043. J Pers Med. 2025. PMID: 39997320 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Canè L., Poto R., Palestra F., Pirozzi M., Parashuraman S., Iacobucci I., Ferrara A.L., La Rocca A., Mercadante E., Pucci P., et al. TSLP is localized in and released from human lung macrophages activated by T2-high and T2-low stimuli: Relevance in asthma and COPD. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024. in press . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

