Imbalance in Unc80 RNA Editing Disrupts Dynamic Neuronal Activity and Olfactory Perception
- PMID: 38892173
- PMCID: PMC11172567
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115985
Imbalance in Unc80 RNA Editing Disrupts Dynamic Neuronal Activity and Olfactory Perception
Abstract
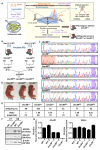
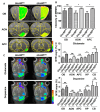
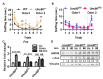
A-to-I RNA editing, catalyzed by the ADAR protein family, significantly contributes to the diversity and adaptability of mammalian RNA signatures, aligning with developmental and physiological needs. Yet, the functions of many editing sites are still to be defined. The Unc80 gene stands out in this context due to its brain-specific expression and the evolutionary conservation of its codon-altering editing event. The precise biological functions of Unc80 and its editing, however, are still largely undefined. In this study, we first demonstrated that Unc80 editing occurs in an ADAR2-dependent manner and is exclusive to the brain. By employing the CRISPR/Cas9 system to generate Unc80 knock-in mouse models that replicate the natural editing variations, our findings revealed that mice with the "gain-of-editing" variant (Unc80G/G) exhibit heightened basal neuronal activity in critical olfactory regions, compared to the "loss-of-editing" (Unc80S/S) counterparts. Moreover, an increase in glutamate levels was observed in the olfactory bulbs of Unc80G/G mice, indicating altered neurotransmitter dynamics. Behavioral analysis of odor detection revealed distinctive responses to novel odors-both Unc80 deficient (Unc80+/-) and Unc80S/S mice demonstrated prolonged exploration times and heightened dishabituation responses. Further elucidating the olfactory connection of Unc80 editing, transcriptomic analysis of the olfactory bulb identified significant alterations in gene expression that corroborate the behavioral and physiological findings. Collectively, our research advances the understanding of Unc80's neurophysiological functions and the impact of its editing on the olfactory sensory system, shedding light on the intricate molecular underpinnings of olfactory perception and neuronal activity.
Keywords: RNA editing; Unc80; neuronal activity; olfactory perception.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A comparative analysis of ADAR mutant mice reveals site-specific regulation of RNA editing.RNA. 2020 Apr;26(4):454-469. doi: 10.1261/rna.072728.119. Epub 2020 Jan 15. RNA. 2020. PMID: 31941663 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of the Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein results in defects of RNA editing of neuronal mRNAs in mouse.RNA Biol. 2017 Nov 2;14(11):1580-1591. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1338232. Epub 2017 Sep 5. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 28640668 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Finger RNA-Binding Protein Zn72D Regulates ADAR-Mediated RNA Editing in Neurons.Cell Rep. 2020 May 19;31(7):107654. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107654. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32433963 Free PMC article.
-
Current strategies for Site-Directed RNA Editing using ADARs.Methods. 2019 Mar 1;156:16-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.11.016. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Methods. 2019. PMID: 30502398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What do editors do? Understanding the physiological functions of A-to-I RNA editing by adenosine deaminase acting on RNAs.Open Biol. 2020 Jul;10(7):200085. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200085. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 32603639 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A-to-I-edited miR-1251-5p restrains tumor growth and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma through regulating TCF7-mediated Wnt signaling pathway.Discov Oncol. 2024 Oct 24;15(1):587. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01462-7. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39446175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Konen L.M., Wright A.L., Royle G.A., Morris G.P., Lau B.K., Seow P.W., Zinn R., Milham L.T., Vaughan C.W., Vissel B. A new mouse line with reduced GluA2 Q/R site RNA editing exhibits loss of dendritic spines, hippocampal CA1-neuron loss, learning and memory impairments and NMDA receptor-independent seizure vulnerability. Mol. Brain. 2020;13:27. doi: 10.1186/s13041-020-0545-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

