Probing the Conformational Restraints of DNA Damage Recognition with β-L-Nucleotides
- PMID: 38892193
- PMCID: PMC11172447
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25116006
Probing the Conformational Restraints of DNA Damage Recognition with β-L-Nucleotides
Abstract
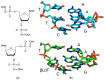
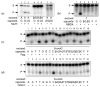
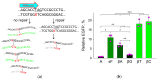
The DNA building blocks 2'-deoxynucleotides are enantiomeric, with their natural β-D-configuration dictated by the sugar moiety. Their synthetic β-L-enantiomers (βLdNs) can be used to obtain L-DNA, which, when fully substituted, is resistant to nucleases and is finding use in many biosensing and nanotechnology applications. However, much less is known about the enzymatic recognition and processing of individual βLdNs embedded in D-DNA. Here, we address the template properties of βLdNs for several DNA polymerases and the ability of base excision repair enzymes to remove these modifications from DNA. The Klenow fragment was fully blocked by βLdNs, whereas DNA polymerase κ bypassed them in an error-free manner. Phage RB69 DNA polymerase and DNA polymerase β treated βLdNs as non-instructive but the latter enzyme shifted towards error-free incorporation on a gapped DNA substrate. DNA glycosylases and AP endonucleases did not process βLdNs. DNA glycosylases sensitive to the base opposite their cognate lesions also did not recognize βLdNs as a correct pairing partner. Nevertheless, when placed in a reporter plasmid, pyrimidine βLdNs were resistant to repair in human cells, whereas purine βLdNs appear to be partly repaired. Overall, βLdNs are unique modifications that are mostly non-instructive but have dual non-instructive/instructive properties in special cases.
Keywords: AP endonucleases; DNA glycosylases; DNA polymerases; DNA repair; translesion synthesis; β-L-nucleotides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Seeman N.C., Sleiman H.F. DNA nanotechnology. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018;3:17068. doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2017.68. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

