Nuclear miRNAs: Gene Regulation Activities
- PMID: 38892257
- PMCID: PMC11172810
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25116066
Nuclear miRNAs: Gene Regulation Activities
Abstract
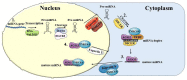
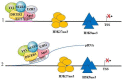
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs which contribute to the regulation of many physiological and pathological processes. Conventionally, miRNAs perform their activity in the cytoplasm where they regulate gene expression by interacting in a sequence-specific manner with mature messenger RNAs. Recent studies point to the presence of mature miRNAs in the nucleus. This review summarizes current findings regarding the molecular activities of nuclear miRNAs. These molecules can regulate gene expression at the transcriptional level by directly binding DNA on the promoter or the enhancer of regulated genes. miRNAs recruit different protein complexes to these regions, resulting in activation or repression of transcription, through a number of molecular mechanisms. Hematopoiesis is presented as a paradigmatic biological process whereby nuclear miRNAs possess a relevant regulatory role. Nuclear miRNAs can influence gene expression by affecting nuclear mRNA processing and by regulating pri-miRNA maturation, thus impacting the biogenesis of miRNAs themselves. Overall, nuclear miRNAs are biologically active molecules that can be critical for the fine tuning of gene expression and deserve further studies in a number of physiological and pathological conditions.
Keywords: RNA processing; gene regulation; hematopoiesis; miRNAs; nuclear localization; transcriptional control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Nuclear microRNAs and their unconventional role in regulating non-coding RNAs.Protein Cell. 2013 May;4(5):325-30. doi: 10.1007/s13238-013-3001-5. Epub 2013 Apr 13. Protein Cell. 2013. PMID: 23584808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of nuclear-enriched miRNAs during mouse granulopoiesis.J Hematol Oncol. 2014 May 15;7:42. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-7-42. J Hematol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24886830 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear functions of mammalian MicroRNAs in gene regulation, immunity and cancer.Mol Cancer. 2018 Feb 22;17(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0765-5. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29471827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenesis and mechanisms of microRNA-mediated gene regulation.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2022 Mar;119(3):685-692. doi: 10.1002/bit.28029. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2022. PMID: 34979040 Review.
Cited by
-
A Practical Guideline for MicroRNA Sequencing Data Analysis in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2883:403-426. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4290-0_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39702719
-
Stress-Related Roles of Exosomes and Exosomal miRNAs in Common Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 29;25(15):8256. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158256. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma-derived exosomal MicroRNA-31 acts as an oncogene by targeting the tumor suppressor RhoBTB1.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Dec 14;317(1):114. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03558-0. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 39673615
-
Opening new frontiers with catalytic nucleic acids in miRNA inhibition.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 23;16:1604711. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1604711. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40626302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL14 mediates the m6A methylation of miR-29a-3p, thereby activating the MAP2K6 signaling pathway and exacerbating the inflammatory response associated with spinal tuberculosis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Jul 8;20(1):625. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-06037-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40629361 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

