On the Cholesterol Raising Effect of Coffee Diterpenes Cafestol and 16- O-Methylcafestol: Interaction with Farnesoid X Receptor
- PMID: 38892285
- PMCID: PMC11173301
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25116096
On the Cholesterol Raising Effect of Coffee Diterpenes Cafestol and 16- O-Methylcafestol: Interaction with Farnesoid X Receptor
Abstract
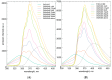
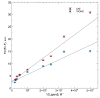
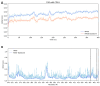
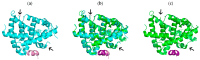
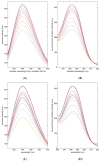
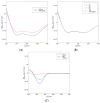
The diterpene cafestol represents the most potent cholesterol-elevating compound known in the human diet, being responsible for more than 80% of the effect of coffee on serum lipids, with a mechanism still not fully clarified. In the present study, the interaction of cafestol and 16-O-methylcafestol with the stabilized ligand-binding domain (LBD) of the Farnesoid X Receptor was evaluated by fluorescence and circular dichroism. Fluorescence quenching was observed with both cafestol and 16-O-methylcafestol due to an interaction occurring in the close environment of the tryptophan W454 residue of the protein, as confirmed by docking and molecular dynamics. A conformational change of the protein was also observed by circular dichroism, particularly for cafestol. These results provide evidence at the molecular level of the interactions of FXR with the coffee diterpenes, confirming that cafestol can act as an agonist of FXR, causing an enhancement of the cholesterol level in blood serum.
Keywords: 16-O-methylcafestol; FXR; cafestol; circular dichroism; coffee; fluorescence.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Elena Guercia and Luciano Navarini were employed by the company illycaffè S.p.A. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




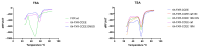






References
-
- Statista Coffee Consumption Worldwide from 2012/13 to 2021/22 with a Forecast to 2022/23. 2023. [(accessed on 31 October 2023)]. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/292595/global-coffee-consumption/
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

