NOS2 and COX-2 Co-Expression Promotes Cancer Progression: A Potential Target for Developing Agents to Prevent or Treat Highly Aggressive Breast Cancer
- PMID: 38892290
- PMCID: PMC11173351
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25116103
NOS2 and COX-2 Co-Expression Promotes Cancer Progression: A Potential Target for Developing Agents to Prevent or Treat Highly Aggressive Breast Cancer
Abstract
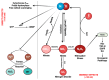
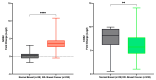
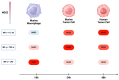
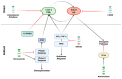
Nitric oxide (NO) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) exert profound biological impacts dictated by their chemistry. Understanding their spatial distribution is essential for deciphering their roles in diverse biological processes. This review establishes a framework for the chemical biology of NO and RNS, exploring their dynamic reactions within the context of cancer. Concentration-dependent signaling reveals distinctive processes in cancer, with three levels of NO influencing oncogenic properties. In this context, NO plays a crucial role in cancer cell proliferation, metastasis, chemotherapy resistance, and immune suppression. Increased NOS2 expression correlates with poor survival across different tumors, including breast cancer. Additionally, NOS2 can crosstalk with the proinflammatory enzyme cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) to promote cancer progression. NOS2 and COX-2 co-expression establishes a positive feed-forward loop, driving immunosuppression and metastasis in estrogen receptor-negative (ER-) breast cancer. Spatial evaluation of NOS2 and COX-2 reveals orthogonal expression, suggesting the unique roles of these niches in the tumor microenvironment (TME). NOS2 and COX2 niche formation requires IFN-γ and cytokine-releasing cells. These niches contribute to poor clinical outcomes, emphasizing their role in cancer progression. Strategies to target these markers include direct inhibition, involving pan-inhibitors and selective inhibitors, as well as indirect approaches targeting their induction or downstream effectors. Compounds from cruciferous vegetables are potential candidates for NOS2 and COX-2 inhibition offering therapeutic applications. Thus, understanding the chemical biology of NO and RNS, their spatial distribution, and their implications in cancer progression provides valuable insights for developing targeted therapies and preventive strategies.
Keywords: biochemistry; breast cancer; nitric oxide; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Somasundaram V., Basudhar D., Bharadwaj G., No J.H., Ridnour L.A., Cheng R.Y.S., Fujita M., Thomas D.D., Anderson S.K., McVicar D.W., et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Nitric Oxide in Cancer Progression, Signal Transduction, and Metabolism. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019;30:1124–1143. doi: 10.1089/ars.2018.7527. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thomas D.D., Heinecke J.L., Ridnour L.A., Cheng R.Y., Kesarwala A.H., Switzer C.H., McVicar D.W., Roberts D.D., Glynn S., Fukuto J.M., et al. Signaling and Stress: The Redox Landscape in NOS2 Biology. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015;87:204–225. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

