The Role of TLR7 and TLR9 in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis
- PMID: 38892317
- PMCID: PMC11172923
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25116133
The Role of TLR7 and TLR9 in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
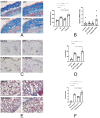
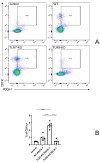
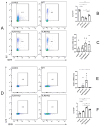
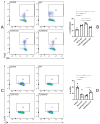
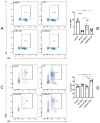
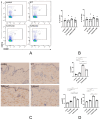
The bleomycin-induced scleroderma model is a well-established and dependable method for creating a mouse model of SSc (systemic sclerosis). In the field of skin connective tissue diseases, increasing evidence from clinical and animal experiments suggests that TLRs (Toll-like receptors) play an important role in several diseases. This study aimed to determine the role of TLR7 (Toll-like receptor 7) and TLR9 (Toll-like receptor 9) in the mechanisms of immune abnormalities and fibrosis in SSc. This study used TLR7-KO mice (TLR7-knockout mice with a balb/c background) and TLR9-KO mice (TLR9-knockout mice with a balb/c background) as well as WT mice (wild-type balb/c mice). All three kinds of mice were induced by BLM (bleomycin) in a scleroderma model as the experimental group; meanwhile, WT mice treated with PBS (phosphate-buffered saline) were used as the control group. We analyzed the fibrotic phenotype and the immunological abnormality phenotype of TLR7-deficient and TLR9-deficient mice in the SSc disease model using flow cytometry, RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction), a histological examination, and IHC (immunohistochemical staining). In a mouse model of SSc disease, the deletion of TLR7 attenuated skin and lung fibrosis, while the deletion of TLR9 exacerbated skin and lung fibrosis. The deletion of TLR7 resulted in a relative decrease in the infiltration and expression of various pro-inflammatory and fibrotic cells and cytokines in the skin. On the other hand, the deletion of TLR9 resulted in a relative increase in the infiltration and expression of various pro-inflammatory and cytokine-inhibiting cells and cytokines in the skin. Under the influence of pDCs (plasmacytoid dendritic cells), the balances of Beff/Breg (IL-6 + CD19 + B cell/IL-10 + CD19 + B cell), Th17/Treg (IL-17A + CD4 + T cell/Foxp3 + CD25 + CD4 + T cell), M1/M2 (CD86 + macrophage/CD206 + macrophage), and Th1/Th2 (TNFα + CD3 + CD4 + T cell/IL-4 + CD3 + CD4 + T cell) were biased towards the suppression of inflammation and fibrosis as a result of the TLR7 deletion. Comparatively, the balance was biased towards promoting inflammation and fibrosis due to the TLR9 deletion. In the SSc model, TLR7 promoted inflammation and fibrosis progression, while TLR9 played a protective role. These results suggest that TLR7 and TLR9 play opposite roles in triggering SSc to produce immune system abnormalities and skin fibrosis.
Keywords: B cells; Effector B cells; Regulatory B cells; TLR7; TLR9; Th17; Toll-like receptors; Treg; pDCs; plasmacytoid dendritic cells; systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yamada T., Ogi K., Sakashita M., Kanno M., Kubo S., Ito Y., Imoto Y., Tokunaga T., Okamoto M., Narita N., et al. Toll-like receptor ligands induce cytokine and chemokine production in human inner ear endolymphatic sac fibroblasts. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017;44:398–403. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2016.10.007. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

