Perspective and Therapeutic Potential of the Noncoding RNA-Connexin Axis
- PMID: 38892334
- PMCID: PMC11173347
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25116146
Perspective and Therapeutic Potential of the Noncoding RNA-Connexin Axis
Abstract
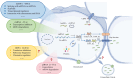
Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) are a class of nucleotide sequences that cannot be translated into peptides. ncRNAs can function post-transcriptionally by splicing complementary sequences of mRNAs or other ncRNAs or by directly engaging in protein interactions. Over the past few decades, the pervasiveness of ncRNAs in cell physiology and their pivotal roles in various diseases have been identified. One target regulated by ncRNAs is connexin (Cx), a protein that forms gap junctions and hemichannels and facilitates intercellular molecule exchange. The aberrant expression and misdistribution of connexins have been implicated in central nervous system diseases, cardiovascular diseases, bone diseases, and cancer. Current databases and technologies have enabled researchers to identify the direct or indirect relationships between ncRNAs and connexins, thereby elucidating their correlation with diseases. In this review, we selected the literature published in the past five years concerning disorders regulated by ncRNAs via corresponding connexins. Among it, microRNAs that regulate the expression of Cx43 play a crucial role in disease development and are predominantly reviewed. The distinctive perspective of the ncRNA-Cx axis interprets pathology in an epigenetic manner and is expected to motivate research for the development of biomarkers and therapeutics.
Keywords: connexin; disease; lncRNA; microRNA; noncoding RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yuan M., Yang B., Rothschild G., Mann J.J., Sanford L.D., Tang X., Huang C., Wang C., Zhang W. Epigenetic regulation in major depression and other stress-related disorders: Molecular mechanisms, clinical relevance and therapeutic potential. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023;8:309. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01519-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Di Martino M.T., Arbitrio M., Caracciolo D., Cordua A., Cuomo O., Grillone K., Riillo C., Caridà G., Scionti F., Labanca C., et al. miR-221/222 as biomarkers and targets for therapeutic intervention on cancer and other diseases: A systematic review. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 2022;27:1191–1224. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.02.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

