Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Quantitative Trait Loci and Candidate Genes Associated with High Interferon-gamma Production in Holstein Cattle Naturally Infected with Mycobacterium Bovis
- PMID: 38892353
- PMCID: PMC11172856
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25116165
Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Quantitative Trait Loci and Candidate Genes Associated with High Interferon-gamma Production in Holstein Cattle Naturally Infected with Mycobacterium Bovis
Abstract
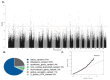
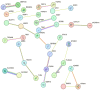
Mycobacterium bovis (Mb) is the causative agent of bovine tuberculosis (bTb). Genetic selection aiming to identify less susceptible animals has been proposed as a complementary measure in ongoing programs toward controlling Mb infection. However, individual animal phenotypes for bTb based on interferon-gamma (IFNɣ) and its use in bovine selective breeding programs have not been explored. In the current study, IFNɣ production was measured using a specific IFNɣ ELISA kit in bovine purified protein derivative (bPPD)-stimulated blood samples collected from Holstein cattle. DNA isolated from the peripheral blood samples collected from the animals included in the study was genotyped with the EuroG Medium Density bead Chip, and the genotypes were imputed to whole-genome sequences. A genome-wide association analysis (GWAS) revealed that the IFNɣ in response to bPPD was associated with a specific genetic profile (heritability = 0.23) and allowed the identification of 163 SNPs, 72 quantitative trait loci (QTLs), 197 candidate genes, and 8 microRNAs (miRNAs) associated with this phenotype. No negative correlations between this phenotype and other phenotypes and traits included in the Spanish breeding program were observed. Taken together, our results define a heritable and distinct immunogenetic profile associated with strong production of IFNɣ in response to Mb.
Keywords: Mycobacterium bovis; breeding; interferon-gamma; polymorphisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association between High Interferon-Gamma Production in Avian Tuberculin-Stimulated Blood from Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis-Infected Cattle and Candidate Genes Implicated in Necroptosis.Microorganisms. 2023 Jul 15;11(7):1817. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071817. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37512987 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of loci associated with susceptibility to Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection in Holstein cattle using combinations of diagnostic tests and imputed whole-genome sequence data.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 27;16(8):e0256091. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256091. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34449805 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of loci associated with pathological outcomes in Holstein cattle infected with Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis using whole-genome sequence data.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 11;11(1):20177. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99672-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34635747 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine tuberculosis: effect of the tuberculin skin test on in vitro interferon gamma responses.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010 Jul;136(1-2):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2010.02.007. Epub 2010 Feb 13. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010. PMID: 20219253 Review.
-
The impact of changing the cut-off threshold of the interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) assay for diagnosing bovine tuberculosis in Ireland.Prev Vet Med. 2024 Mar;224:106129. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2024.106129. Epub 2024 Jan 20. Prev Vet Med. 2024. PMID: 38325115 Review.
References
-
- Olea-Popelka F., Muwonge A., Perera A., Dean A.S., Mumford E., Erlacher-Vindel E., Forcella S., Silk B.J., Ditiu L., El Idrissi A., et al. Zoonotic Tuberculosis in Human Beings Caused by Mycobacterium bovis—A Call for Action. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017;17:e21–e25. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30139-6. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

