Optimizing Messenger RNA Analysis Using Ultra-Wide Pore Size Exclusion Chromatography Columns
- PMID: 38892442
- PMCID: PMC11172508
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25116254
Optimizing Messenger RNA Analysis Using Ultra-Wide Pore Size Exclusion Chromatography Columns
Abstract
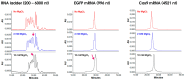
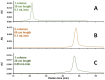
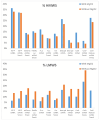
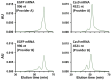
Biopharmaceutical products, in particular messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA), have the potential to dramatically improve the quality of life for patients suffering from respiratory and infectious diseases, rare genetic disorders, and cancer. However, the quality and safety of such products are particularly critical for patients and require close scrutiny. Key product-related impurities, such as fragments and aggregates, among others, can significantly reduce the efficacy of mRNA therapies. In the present work, the possibilities offered by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) for the characterization of mRNA samples were explored using state-of-the-art ultra-wide pore columns with average pore diameters of 1000 and 2500 Å. Our investigation shows that a column with 1000 Å pores proved to be optimal for the analysis of mRNA products, whatever the size between 500 and 5000 nucleotides (nt). We also studied the influence of mobile phase composition and found that the addition of 10 mM magnesium chloride (MgCl2) can be beneficial in improving the resolution and recovery of large size variants for some mRNA samples. We demonstrate that caution should be exercised when increasing column length or decreasing the flow rate. While these adjustments slightly improve resolution, they also lead to an apparent increase in the amount of low-molecular-weight species (LMWS) and monomer peak tailing, which can be attributed to the prolonged residence time inside the column. Finally, our optimal SEC method has been successfully applied to a wide range of mRNA products, ranging from 1000 to 4500 nt in length, as well as mRNA from different suppliers and stressed/unstressed samples.
Keywords: aggregates; fragments; messenger RNA; size exclusion chromatography; ultra-wide pore.
Conflict of interest statement
ACQUITY, UPLC, Empower, BEH, and GTxResolve are trademarks of Waters Technologies Corporation. CleanCap is a trademark of TriLink BioTechnologies, LLC. Milli-Q is a trademark of Merck KGaA.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Systematic comparison of wide pore size exclusion chromatography columns for the characterization of gene therapy products.J Chromatogr A. 2025 Jul 5;1752:465972. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2025.465972. Epub 2025 Apr 16. J Chromatogr A. 2025. PMID: 40273568
-
Separation of Plasmid DNA Topological Forms, Messenger RNA, and Lipid Nanoparticle Aggregates Using an Ultrawide Pore Size Exclusion Chromatography Column.Anal Chem. 2023 Oct 10;95(40):15017-15024. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c02944. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37747361 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical performance of multiple size-exclusion chromatography columns connected in series.J Chromatogr A. 2020 Dec 20;1634:461673. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461673. Epub 2020 Nov 2. J Chromatogr A. 2020. PMID: 33189963
-
Size exclusion chromatography of biopharmaceutical products: From current practices for proteins to emerging trends for viral vectors, nucleic acids and lipid nanoparticles.J Chromatogr A. 2024 May 10;1722:464862. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2024.464862. Epub 2024 Apr 1. J Chromatogr A. 2024. PMID: 38581978 Review.
-
Unraveling the mysteries of modern size exclusion chromatography - the way to achieve confident characterization of therapeutic proteins.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2018 Aug 15;1092:368-378. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.06.029. Epub 2018 Jun 18. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29936373 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Impact of In Vitro-Transcribed mRNA Impurities on Cellular Responses.Anal Chem. 2024 Nov 5;96(44):17789-17799. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c04162. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39445393
-
Keeping up with a Quickly Diversifying Pharmaceutical Landscape.ACS Meas Sci Au. 2024 Sep 24;4(6):615-619. doi: 10.1021/acsmeasuresciau.4c00050. eCollection 2024 Dec 18. ACS Meas Sci Au. 2024. PMID: 39713029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Throughput Quantification and Characterization of Dual Payload mRNA/LNP Cargo via Deformulating Size Exclusion and Ion Pairing Reversed Phase Assays.Anal Chem. 2025 Feb 11;97(5):3091-3098. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c06296. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 39883007 Free PMC article.
-
Proof of Concept Application of Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography for Direct Online Disruption of Lipid Nanoparticles, Intact mRNA Analysis, and Measure of Encapsulation Efficiency.Anal Chem. 2025 Apr 15;97(14):7627-7632. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5c00565. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40167235 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation and analysis of mRNA critical quality attributes using liquid chromatography based methods.J Chromatogr A. 2025 Mar 29;1745:465724. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2025.465724. Epub 2025 Jan 28. J Chromatogr A. 2025. PMID: 39946818 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2023. Press Release. NobelPrize.Org. Nobel Prize Outreach AB 2024. 2023. [(accessed on 2 May 2024)]. Available online: https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/2023/press-release/
-
- Ichihashi Y., Fukushima A., Shibata A., Shirasu K. High Impact Gene Discovery: Simple Strand-Specific mRNA Library Construction and Differential Regulatory Analysis Based on Gene Co-Expression Network. In: Yamaguchi N., editor. Plant Transcription Factors. Volume 1830. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2018. pp. 163–189. Methods in Molecular Biology. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

