Small Molecule Therapeutics in the Pipeline Targeting for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Origin, Challenges, Opportunities, and Mechanisms of Action
- PMID: 38892472
- PMCID: PMC11172743
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25116285
Small Molecule Therapeutics in the Pipeline Targeting for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Origin, Challenges, Opportunities, and Mechanisms of Action
Abstract
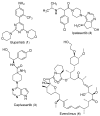
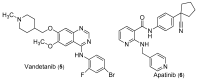
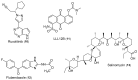
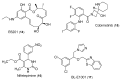
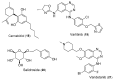
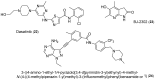
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells are devoid of estrogen receptors (ERs), progesterone receptor (PRs), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and it (TNBC) counts for about 10-15% of all breast cancers. TNBC is highly invasive, having a faster growth rate and a higher risk of metastasis and recurrence. Still, chemotherapy is one of the widely used options for treating TNBC. This study reviewed the histological and molecular characterization of TNBC subtypes, signaling pathways that are aberrantly expressed, and small molecules targeting these pathways, as either single agents or in combination with other therapeutic agents like chemotherapeutics, immunotherapeutics, and antibody-drug conjugates; their mechanisms of action, challenges, and future perspectives were also reviewed. A detailed analytical review was carried out using the literature collected from the SciFinder, PubMed, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar, ACS, Springer, and Wiley databases. Several small molecule inhibitors were found to be therapeutics for treating TNBC. The mechanism of action and the different signaling pathways through which the small molecules exert their effects were studied, including clinical trials, if reported. These small molecule inhibitors include buparlisib, everolimus, vandetanib, apatinib, olaparib, salidroside, etc. Some of the signaling pathways involved in TNBC, including the VEGF, PARP, STAT3, MAPK, EGFR, P13K, and SRC pathways, were discussed. Due to the absence of these biomarkers, drug development for treating TNBC is challenging, with chemotherapy being the main therapeutic agent. However, chemotherapy is associated with chemoresistance and a high toxicity to healthy cells as side effects. Hence, there is a continuous demand for small-molecule inhibitors that specifically target several signaling pathways that are abnormally expressed in TNBC. We attempted to include all the recent developments in this field. Any omission is truly unintentional.
Keywords: breast cancer; chemoresistance; chemotherapy; estrogen receptor; human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; immunotherapy; progesterone receptor; signaling pathways; small molecules; triple-negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
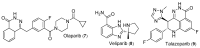
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

