Seasonality Affects Fluid Intake Behaviors among Young Adults in Hebei, China
- PMID: 38892476
- PMCID: PMC11173941
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16111542
Seasonality Affects Fluid Intake Behaviors among Young Adults in Hebei, China
Abstract
Background: Evidence on the association between environmental factors and fluid intake behavior remains limited. The current study aims to explore seasonal variations in fluid intake behaviors among young adults in China.
Methods: A prospective cohort of 79 healthy young adults (43 males and 36 females) aged 19-21 in Hebei, China, was assessed for fluid intake behaviors for four seasons. For each assessment, the participants' anthropometric measurements were collected. Temperature and humidity on survey days were measured. Participants' total drinking fluid (TDF) was recorded using a self-administrative 7 d, 24 h fluid intake questionnaire. To calculate water from food (WFF), we weighed all foods consumed by participants. Duplicates of consumed food samples were collected to measure the water content via the drying method.
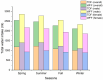
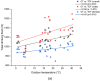
Results: The mean total water intake (TWI) was 2761 ± 881, 2551 ± 845, 2210 ± 551, and 1989 ± 579 for spring, summer, fall, and winter, respectively (F(2.37) = 42.29, p < 0.001). The volume and proportion of TWI from TDF and WFF varied across the four seasons. The volume of WFF in spring (1361 ± 281, F(2.61) = 17.21, p < 0.001) and TDF in summer (1218 ± 502, F(2.62) = 9.36, p < 0.001) was among the highest, while participants' fluid intake behaviors in spring and summer were less distinct than the other pairwise comparisons. A moderate association was found between outdoor temperature and TDF (r = 0.53, p < 0.01). Different general estimating equations suggested that gender, seasonality, outdoor temperature, differences in indoor and outdoor temperature, and mean temperature were independent factors of TDF. An interactive effect was found for gender and temperature, showing that the expected TDF of males may increase more as the temperature climbs.
Conclusions: Gender, seasonality, and air temperature could significantly affect fluid intake behaviors, including the amount and type of fluid intake. However, the independent effect of BMI and humidity remains unclear.
Keywords: drinking fluid; fluid intake; seasonality; temperature; water from food.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Institute of Medicine . Dietary Reference Intakes for Water, Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, and Sulfate. The National Academies Press; Washington, DC, USA: 2005. pp. 73–185.
-
- Zhang N., Zhang J., Wang X., Li Y., Yan Y., Ma G. Behaviors of Water Intake, Hydration Status, and Related Hydration Biomarkers among Physically Active Male Young Adults in Beijing, China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022;2022:9436186. doi: 10.1155/2022/9436186. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

