Therapeutic Effects of Plant Anthocyanin against Alzheimer's Disease and Modulate Gut Health, Short-Chain Fatty Acids
- PMID: 38892488
- PMCID: PMC11173718
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16111554
Therapeutic Effects of Plant Anthocyanin against Alzheimer's Disease and Modulate Gut Health, Short-Chain Fatty Acids
Abstract
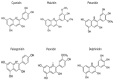
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia and neurogenerative disease (NDD), and it is also one of the leading causes of death worldwide. The number of AD patients is over 55 million according to 2020 Alzheimer's Disease International (ADI), and the number is increasing drastically without any effective cure. In this review, we discuss and analyze the potential role of anthocyanins (ACNs) against AD while understanding the molecular mechanisms. ACNs have been reported as having neuroprotective effects by mitigating cognitive impairments, apoptotic markers, neuroinflammation, aberrant amyloidogenesis, and tauopathy. Taken together, ACNs could be an important therapeutic agent for combating or delaying the onset of AD.
Keywords: Aβ and tau; SCFAs; anthocyanins; cognition; neuroprotection; plant bioactive.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Beong Ou Lim was employed by the Human Bioscience Corp. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical