The Effects of Antioxidant Supplementation on the Pathologic Mechanisms of Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease Development
- PMID: 38892574
- PMCID: PMC11175159
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16111641
The Effects of Antioxidant Supplementation on the Pathologic Mechanisms of Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease Development
Abstract
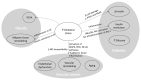
In people with obesity, diabetes, and hypertension, lipid and glucose metabolism and oxidative stress generation interact. This condition, known as a "metabolic syndrome" (MetS), presents a global challenge and appears to be the underlying mechanism for the development of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). This review is designed based on evidence indicating the pathogenic mechanisms of MetS. In detail, we will look at the mechanisms of oxidative stress induction in MetS, the effects of elevated oxidative stress levels on the condition's pathophysiology, and matters related to endothelial function. According to different components of the MetS pathophysiological network, the effects of antioxidants and endothelial dysfunction are reviewed. After considering the strategic role of oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of MetS and its associated CVDs, oxidative stress management by antioxidant supplementation seems an appropriate therapeutic approach.
Keywords: antioxidant supplementation; hypertension; metabolic syndrome; obesity; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mohamed S.M., Shalaby M.A., El-shiekh R.A., El-banna H.A., Emam S.R., Bakr A.F. Metabolic syndrome: Risk factors, diagnosis, pathogenesis, and management with natural approaches. Food Chem. Adv. 2023;3:100335. doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2023.100335. - DOI
-
- Cojocaru K.A., Luchian I., Goriuc A., Antoci L.M., Ciobanu C.G., Popescu R., Vlad C.-E., Blaj M., Foia L.G. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Therapeutic Strategies in Diabetes, Obesity, and Cardiovascular Disease. Antioxidants. 2023;12:658. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030658. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

