Therapeutic Effects of Natural Products on Liver Cancer and Their Potential Mechanisms
- PMID: 38892575
- PMCID: PMC11174683
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16111642
Therapeutic Effects of Natural Products on Liver Cancer and Their Potential Mechanisms
Abstract
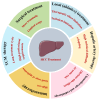
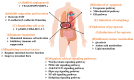
Liver cancer ranks third globally among causes of cancer-related deaths, posing a significant public health challenge. However, current treatments are inadequate, prompting a growing demand for novel, safe, and effective therapies. Natural products (NPs) have emerged as promising candidates in drug development due to their diverse biological activities, low toxicity, and minimal side effects. This paper begins by reviewing existing treatment methods and drugs for liver cancer. It then summarizes the therapeutic effects of NPs sourced from various origins on liver cancer. Finally, we analyze the potential mechanisms of NPs in treating liver cancer, including inhibition of angiogenesis, migration, and invasion; regulation of the cell cycle; induction of apoptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis, and ferroptosis; influence on tumor metabolism; immune regulation; regulation of intestinal function; and regulation of key signaling pathways. This systematic review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of NPs research in liver cancer treatment, offering a foundation for further development and application in pharmaceuticals and functional foods.
Keywords: liver cancer; mechanisms of action; natural products; therapeutic drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Advances in antitumor activity and mechanism of natural steroidal saponins: A review of advances, challenges, and future prospects.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jun;128:155432. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155432. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38518645
-
Advancements in the therapeutic potential of sesquiterpenoids for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (Review).Int J Oncol. 2025 Jul;67(1):60. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5766. Epub 2025 Jun 20. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40539465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Anticancer Potential of [Formula: see text]-Sitosterol: A Comprehensive Exploration of Mechanisms and Therapeutic Prospects.Am J Chin Med. 2025;53(4):1241-1263. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X2550048X. Epub 2025 Jun 17. Am J Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40582720 Review.
Cited by
-
Herbal Medicine: Enhancing the Anticancer Potential of Natural Products in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy Through Advanced Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2025 May 20;17(5):673. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17050673. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40430962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyketides and alkaloids from the fungus Aspergillus Fumigatus YB4-17 and ent-Fumiquinazoline J induce apoptosis, paraptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 4;15:1487977. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1487977. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39720587 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing Cancer Treatment Through Gut Microbiome Modulation.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 7;17(7):1252. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071252. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin inhibits the activity of ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 to promote NLRP3‑dependent pyroptosis in non‑small cell lung cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2025 Mar;66(3):21. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5727. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39950328 Free PMC article.
-
Prunin: An Emerging Anticancer Flavonoid.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 16;26(6):2678. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062678. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141319 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pinter M., Sieghart W., Graziadei I., Vogel W., Maieron A., Königsberg R., Weissmann A., Kornek G., Plank C., Peck-Radosavljevic M. Sorafenib in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma from mild to advanced stage liver cirrhosis. Oncol. 2009;14:70–76. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2008-0191. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

