Potential of Titanium Pins Coated with Fibroblast Growth Factor-2-Calcium Phosphate Composite Layers to Reduce the Risk of Impaired Bone-Pin Interface Strength in the External Fixation of Distal Radius Fractures
- PMID: 38892751
- PMCID: PMC11172767
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13113040
Potential of Titanium Pins Coated with Fibroblast Growth Factor-2-Calcium Phosphate Composite Layers to Reduce the Risk of Impaired Bone-Pin Interface Strength in the External Fixation of Distal Radius Fractures
Abstract
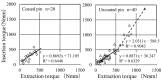
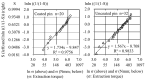
Background: The risk of impaired bone-pin interface strength in titanium (Ti) pins coated with fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-calcium phosphate (CP) composite layers is yet to be evaluated in a clinical study. This retrospective study used Weibull plot analysis to evaluate bone-pin interface strength in Ti pins coated with FGF-CP layers for external distal radius fracture fixation. Methods: The distal radial fractures were treated with external fixation. The FGF-CP group comprised five patients (all women, aged 70.4 ± 5.9 (range: 62-77) years), and the uncoated pin group comprised ten patients (eight women and two men, aged 64.4 ± 11.7 (range: 43-83) years). The pins were removed after six weeks. The insertion and extraction peak torques were measured. The extraction peak torque was evaluated using Weibull plot analysis. Results: We compared the extraction torque of the two groups at or below 506 Nmm for a fair comparison using Weibull plot analysis. The Weibull plots were linear for both the FGF-CP and uncoated pin groups. The slope of the regression line was significantly higher in the FGF-CP group (1.7343) than in the uncoated pin group (1.5670) (p = 0.011). The intercept of the regression line was significantly lower in the FGF-CP group (-9.847) than in the uncoated pin group (-8.708) (p = 0.002). Thus, the two regression lines significantly differed. Conclusions: Ti pins coated with FGF-CP layers exhibit the potential to reduce the risk of impaired bone-pin interface strength in the external fixation of distal radius fractures.
Keywords: Weibull plot analysis; calcium phosphate; coating; distal radius fractures; external fixation; fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2); impaired bone fixation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Initial clinical trial of pins coated with fibroblast growth factor-2-apatite composite layer in external fixation of distal radius fractures.J Orthop. 2018 Dec 20;16(1):69-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2018.12.012. eCollection 2019 Jan-Feb. J Orthop. 2018. PMID: 30662242 Free PMC article.
-
Do Stainless-Steel Pins Coated with Fibroblast Growth Factor-Calcium Phosphatase Composite Layers Have Anti-Infective Effects?Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Aug 30;60(9):1419. doi: 10.3390/medicina60091419. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39336460 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of the bone-pin interface strength in osteoporotic bone with use of hydroxyapatite-coated tapered external-fixation pins. A prospective, randomized clinical study of wrist fractures.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001 May;83(5):717-21. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200105000-00010. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. PMID: 11379741 Clinical Trial.
-
State of the art review: techniques to avoid pin loosening and infection in external fixation.J Orthop Trauma. 2002 Mar;16(3):189-95. doi: 10.1097/00005131-200203000-00009. J Orthop Trauma. 2002. PMID: 11880783 Review.
-
Hydroxyapatite-coated external fixation pins.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2005 Jul;2(4):465-71. doi: 10.1586/17434440.2.4.465. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2005. PMID: 16293085 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

