Contemporary Management of the Failing Fontan
- PMID: 38892760
- PMCID: PMC11172880
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13113049
Contemporary Management of the Failing Fontan
Abstract
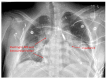
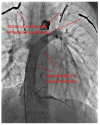
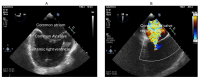
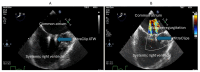
Adult patients with congenital heart disease have now surpassed the pediatric population due to advances in surgery and improved survival. One such complex congenital heart disease seen in adult patients is the Fontan circulation. These patients have complex physiology and are at risk for several complications, including thrombosis of the Fontan pathway, pulmonary vascular disease, heart failure, atrial arrhythmias, atrioventricular valve regurgitation, and protein-losing enteropathy. This review discusses the commonly encountered phenotypes of Fontan circulatory failure and their contemporary management.
Keywords: Fontan circulation; Fontan failure; congenital heart disease; single ventricle physiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

