Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Magnesium Sulfate in Spinal Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38892833
- PMCID: PMC11172721
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13113122
Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Magnesium Sulfate in Spinal Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Optimizing pain management in spinal surgery is crucial for preventing adverse events due to delayed mobilization. Magnesium sulfate has potential benefits in spinal surgery because of its analgesic properties and modulation of neurotransmitters and autonomic nervous system. Existing evidence regarding the use of magnesium sulfate is partial and controversial, necessitating a comprehensive meta-analysis to evaluate its efficacy and safety. The aim of this study was to conduct a comprehensive meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy and safety of magnesium sulfate in spinal surgery compared to other available options. This meta-analysis adhered to the PRISMA guidelines. Patients undergoing spinal surgery were included, with the intervention group receiving intravenous magnesium sulfate (MS) at various doses or combinations, whereas the comparison group received other alternatives or a placebo. The efficacy and safety outcomes were assessed. Data were collected from multiple databases and analyzed using Review Manager version 5.4. Heterogeneity was assessed and fixed- or random-effects models were applied. The meta-analysis included eight studies (n = 541). Magnesium sulfate demonstrated significant reductions in pain at 24 h (MD -0.20, 95% CI: -0.39 to -0.02) and opioid consumption (SMD -0.66, 95% CI: -0.95 to -0.38) compared to placebo. Additionally, a decrease in the use of muscle relaxants (SMD -0.91, 95% CI: -1.65 to -0.17) and remifentanil (SMD -1.52, 95% CI: -1.98 to -1.05) was observed. In contrast, an increase in extubation time (MD 2.42, 95% CI: 1.14 to 3.71) and verbal response (MD 1.85, 95% CI: 1.13 to 2.58) was observed compared to dexmedetomidine. In conclusion, magnesium sulfate administration in spinal surgery reduced pain and opioid consumption, and prolonged orientation and verbal response. No significant differences in blood pressure or heart rate were observed between the groups.
Keywords: magnesium sulfate; meta-analysis; multimodal; opioid consumption; pain; spinal surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
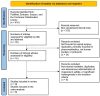






References
-
- Helm Ii S., Harmon P.C., Noe C., Calodney A.K., Abd-Elsayed A., Knezevic N.N., Racz G.B. Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Efficacy and Safety. Pain Physician. 2021;24:S209–S232. - PubMed
-
- Andrade R.R., Oliveira-Neto O.B., Barbosa L.T., Santos I.O., Sousa-Rodrigues C.F., Barbosa F.T. Efetividade da ozonioterapia comparada a outras terapias para dor lombar: Revisão sistemática com metanálise de ensaios clínicos randomizados [Effectiveness of ozone therapy compared to other therapies for low back pain: A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials] Braz. J. Anesthesiol. 2019;69:493–501. doi: 10.1016/j.bjan.2019.06.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

