Evaluating Treatment Outcomes for Pelvic Insufficiency Fractures: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38892887
- PMCID: PMC11172805
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13113176
Evaluating Treatment Outcomes for Pelvic Insufficiency Fractures: A Systematic Review
Abstract
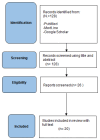
Background: Pelvic insufficiency fractures (PIF) are typical in geriatric populations with reduced bone quality, most commonly in elderly postmenopausal women. These fractures are usually caused by low-energy forces over the bones during ordinary life and cause disabling pain. Treatment options range from conservative to operative. The aim of this study is to assess the outcomes of treatments for pelvic insufficiency fractures, determining optimal approaches between surgical intervention and conservative management. Methods: This literature review systematically examines articles focusing on patients with PIF, following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines, and using PubMed, Medline, and the Cochrane Library database. We took into account only full-text articles in indexed journals with available English abstracts, considering data about patient demographics, surgery, and outcomes. Results: After screening 128 articles, this study reviewed 20 manuscripts involving 1499 patients, mostly elderly females and focusing on sacrum fractures. Common treatments included conservative methods and sacroplasty, with a few complications reported. Osteoporosis was the prevalent comorbidity, and the survival rate post-treatment was high at 92.3%. Mobility outcomes varied, with some patients experiencing significant autonomy loss. The average follow-up period was over 17 months. Conclusions: This study found a cautious approach to surgery (timing of three weeks), which is reserved only for specific patterns, and it leads to increased autonomy and a lower risk of mortality. Due to the lack of pre- and postoperative scores as well as conflicting results, it is imperative to undertake further studies and research to be able to compare the alternative treatments efficiently.
Keywords: fragility fractures; insufficiency fracture; pelvic fracture; sacral fractures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Similar articles
-
Comparative outcome of different treatment options for fragility fractures of the sacrum.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 Dec 19;23(1):1106. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-06039-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 36536363 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous vertebroplasty for treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(19):1-45. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074396 Free PMC article.
-
Utilization of DXA Bone Mineral Densitometry in Ontario: An Evidence-Based Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(20):1-180. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074491 Free PMC article.
-
Indications for surgical fixation of low-energy pelvic ring fractures in elderly: a systematic review.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023 May;143(5):2417-2428. doi: 10.1007/s00402-022-04438-w. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023. PMID: 35462589 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Sacral Insufficiency Fractures: Treatment Modalities and Outcomes.Cureus. 2023 Jul 11;15(7):e41745. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41745. eCollection 2023 Jul. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37575865 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fragility Fractures of the Pelvis-Current Understanding and Open Questions.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 18;14(14):5122. doi: 10.3390/jcm14145122. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40725815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andresen J.R., Prokop A., Wollny M., Radmer S., Schober H.C., Andresen R. Clinical outcome and revenue situation after conservative, interventional and surgical/osteosynthetic treatment of sacral insufficiency fractures. Unfallchirurg. 2021;124:588–597. doi: 10.1007/s00113-020-00932-1. (In German) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources