A Lower Remote Dielectric Sensing Value Was Associated with Hypovolemia and Worse Clinical Outcomes
- PMID: 38892956
- PMCID: PMC11172818
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13113245
A Lower Remote Dielectric Sensing Value Was Associated with Hypovolemia and Worse Clinical Outcomes
Abstract
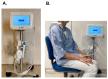
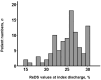
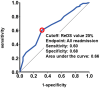
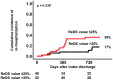
Background: Remote dielectric sensing (ReDS) systems can estimate the amount of lung fluid non-invasively and easily without expert techniques. The correlation between the elevated ReDS value and other modalities that estimate pulmonary congestion has been validated. The clinical implications of lower ReDS values, which may indicate hypovolemia, remain unknown. Methods: A total of 138 patients who were hospitalized for various cardiovascular-related problems and underwent ReDS value measurements at the index discharge in a blinded manner to the attending clinicians were eligible for inclusion. Patients with ReDS values > 30%, indicating the presence of pulmonary congestion, were excluded. The prognostic impact of lower ReDS values on all-cause readmission after index discharge was evaluated. Results: A total of 97 patients were included. The median age was 78 years, and 48 were men. The median ReDS value at index discharge was 26% (23%, 27%). A lower ReDS value correlated with smaller inferior vena cava maximum diameters (r = 0.46, p < 0.001) and higher blood urea nitrogen/creatinine ratios (r = -0.35, p < 0.001). A lower ReDS value (≤25%) was associated with a risk of all-cause readmissions with an unadjusted hazard ratio of 2.68 (95% confidence interval 1.09-6.59, p = 0.031) and an adjusted hazard ratio of 2.30 (95% confidence interval 0.92-5.78, p = 0.076). Its calculated cutoff of 25% significantly stratified the cumulative incidence of the primary outcome (36% versus 17%, p = 0.038). Conclusions: A lower ReDS value may indicate hypovolemia and be associated with the risk of all-cause readmission in patients hospitalized for cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: congestion; diuretics; heart failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

