Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Sleep Disorders: Culprit in Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 38892965
- PMCID: PMC11173264
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13113254
Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Sleep Disorders: Culprit in Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
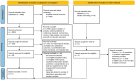
Background: Over the past decade, the gut microbiome (GM) has progressively demonstrated to have a central role in human metabolism, immunity, and cardiometabolic risk. Likewise, sleep disorders showed an impact on individual health and cardiometabolic risk. Recent studies seem to suggest multi-directional relations among GM, diet, sleep, and cardiometabolic risk, though specific interactions are not fully elucidated. We conducted a systematic review to synthesize the currently available evidence on the potential interactions between sleep and GM and their possible implications on cardiometabolic risk. Methods: A systematic review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses, including articles from January 2016 until November 2022. Narrative syntheses were employed to describe the results. Results: A total of 8 studies were selected according to these criteria. Our findings indicated that the sleep disorder and/or the acute circadian rhythm disturbance caused by sleep-wake shifts affected the human GM, mainly throughout microbial functionality. Conclusions: Sleep disorders should be viewed as cardiovascular risk factors and targeted for preventive intervention. More research and well-designed studies are needed to completely assess the role of sleep deprivation in the multi-directional relationship between GM and cardiometabolic risk.
Keywords: PRISMA; cardiometabolic risk; cardiovascular risk; gut microbiome; sleep disorders; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lechner K., Von Schacky C., McKenzie A.L., Worm N., Nixdorff U., Lechner B., Kränkel N., Halle M., Krauss R.M., Scherr J. Lifestyle factors and high-risk atherosclerosis: Pathways and mechanisms beyond traditional risk factors. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020;27:394–406. doi: 10.1177/2047487319869400. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chaput J.P., Dutil C., Featherstone R., Ross R., Giangregorio L., Saunders T.J., Janssen I., Poitras V.J., Kho M.E., Ross-White A., et al. Sleep duration and health in adults: An overview of systematic reviews. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020;45((Suppl. S2)):S218–S231. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2020-0034. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous