Hospitalizations for Acute Otitis and Sinusitis in Patients Living with HIV: A Retrospective Analysis of a Tertiary Center in Romania
- PMID: 38893057
- PMCID: PMC11172890
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13113346
Hospitalizations for Acute Otitis and Sinusitis in Patients Living with HIV: A Retrospective Analysis of a Tertiary Center in Romania
Abstract
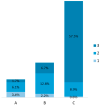
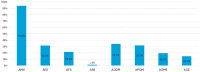
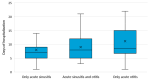
Background/Objectives: Acute or chronic ear, nose and throat (ENT) conditions in people living with HIV can lead to hospitalization and affect their quality of life. The aim of our study was to determine the frequency and characteristics of hospitalizations for acute sinusitis (AS) and acute otitis (AO) in people living with HIV. Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis over the course of six years (from January 2018 to December 2023), assessing all hospitalizations for AS and/or AO occurring in patients living with HIV, at the largest infectious diseases hospital in Romania. Results: We identified a total of 179 cases, among which 149 cases (83.2%) were attributed to AS and 41 cases (22.9%) were due to AO. Among cases of AS, maxillary sinuses were most frequently involved (n = 140/149, 94.0%), and among cases of AO, acute congestive otitis media (n = 14, 34.1%) and acute purulent otitis media (n = 13, 31.7%) were the most common forms. The underlying HIV infection was classified as stage C3 in 57.5% of cases. In 19.6% of cases, it was possible to identify either the trigger or the etiological agent, and the most frequent bacterial pathogens were Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Conclusions: In conclusion, this study highlights that hospitalizations due to acute sinus and ear involvement are not isolated events in people living with HIV. A prospective follow-up is needed to gain a deeper and more dynamic understanding of how ENT health is affected in people with HIV infection. Furthermore, promoting prevention through vaccination may reduce to a certain extent the burden of ENT infections in this population.
Keywords: HIV; acute otitis; acute sinusitis; hospitalization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Global HIV Programme: HIV Data and Statistics 2023. [(accessed on 18 April 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-programmes/hiv/s....
-
- Rein S.M., Lampe F.C., Johnson M.A., Bhagani S., Miller R.F., Chaloner C., Phillips A.N., Burns F.M., Smith C.J. All-cause hospitalization according to demographic group in people living with HIV in the current antiretroviral therapy era. AIDS. 2021;35:245–255. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002750. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu Y., Hao Y., Xiao J., Wu L., Liang H., Han J., Zhao H. Trends in rates and causes of hospitalization among people living with HIV in the antiretroviral therapy era: A retrospective cohort study in China, 2008–2020. Front. Public Health. 2022;10:1000942. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1000942. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ramos-Rincon J.-M., Menchi-Elanzi M., Pinargote-Celorio H., Mayoral A., González-Alcaide G., de Mendoza C., Barreiro P., Gómez-Gallego F., Corral O., Soriano V. Trends in hospitalizations and deaths in HIV-infected patients in Spain over two decades. AIDS. 2022;36:249–256. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000003105. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shija P.S., Karaba J.A., Philemon R.N., Minja B.L., Mtenga P.P., Katundu D.R. Prevalence of Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Manifestations Among HIV Seropositive Patients at a Tertiary Hospital in Northern Tanzania: A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study. HIV AIDS. 2020;12:425–429. doi: 10.2147/HIV.S260908. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

