Practical Application of Deep Learning in Diagnostic Neuropathology-Reimagining a Histological Asset in the Era of Precision Medicine
- PMID: 38893099
- PMCID: PMC11171052
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16111976
Practical Application of Deep Learning in Diagnostic Neuropathology-Reimagining a Histological Asset in the Era of Precision Medicine
Abstract
In the past few decades, neuropathology has experienced several paradigm shifts with the introduction of new technologies. Deep learning, a rapidly progressing subfield of machine learning, seems to be the next innovation to alter the diagnostic workflow. In this review, we will explore the recent changes in the field of neuropathology and how this has led to an increased focus on molecular features in diagnosis and prognosis. Then, we will examine the work carried out to train deep learning models for various diagnostic tasks in neuropathology, as well as the machine learning frameworks they used. Focus will be given to both the challenges and successes highlighted therein, as well as what these trends may tell us about future roadblocks in the widespread adoption of this new technology. Finally, we will touch on recent trends in deep learning, as applied to digital pathology more generally, and what this may tell us about the future of deep learning applications in neuropathology.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; deep learning; neuropathology.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Stephen Yip is a member of advisory boards for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Janssen, Pfizer, and Roche.
Figures
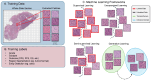
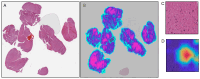
References
-
- Louis D.N., Perry A., Wesseling P., Brat D.J., Cree I.A., Figarella-Branger D., Hawkins C., Ng H.K., Pfister S.M., Reifenberger G., et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro-Oncology. 2021;23:1231–1251. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noab106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zülch K.J. Histological Typing of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 1979. International histological classification of tumours.
-
- Aldape K., Simmons M.L., Davis R.L., Miike R., Wiencke J., Barger G., Lee M., Chen P., Wrensch M. Discrepancies in Diagnoses of Neuroepithelial Neoplasms: The San Francisco Bay Area Adult Glioma Study. Cancer. 2000;88:2342–2349. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(20000515)88:10<2342::AID-CNCR19>3.0.CO;2-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Louis D.N., Perry A., Reifenberger G., Von Deimling A., Figarella-Branger D., Cavenee W.K., Ohgaki H., Wiestler O.D., Kleihues P., Ellison D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:803–820. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

