Using Patient-Specific 3D Modeling and Simulations to Optimize Microwave Ablation Therapy for Liver Cancer
- PMID: 38893214
- PMCID: PMC11171243
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16112095
Using Patient-Specific 3D Modeling and Simulations to Optimize Microwave Ablation Therapy for Liver Cancer
Abstract
Microwave ablation (MWA) of liver tumors presents challenges like under- and over-ablation, potentially leading to inadequate tumor destruction and damage to healthy tissue. This study aims to develop personalized three-dimensional (3D) models to simulate MWA for liver tumors, incorporating patient-specific characteristics. The primary objective is to validate the predicted ablation zones compared to clinical outcomes, offering insights into MWA before therapy to facilitate accurate treatment planning. Contrast-enhanced CT images from three patients were used to create 3D models. The simulations used coupled electromagnetic wave propagation and bioheat transfer to estimate the temperature distribution, predicting tumor destruction and ablation margins. The findings indicate that prolonged ablation does not significantly improve tumor destruction once an adequate margin is achieved, although it increases tissue damage. There was a substantial overlap between the clinical ablation zones and the predicted ablation zones. For patient 1, the Dice score was 0.73, indicating high accuracy, with a sensitivity of 0.72 and a specificity of 0.76. For patient 2, the Dice score was 0.86, with a sensitivity of 0.79 and a specificity of 0.96. For patient 3, the Dice score was 0.8, with a sensitivity of 0.85 and a specificity of 0.74. Patient-specific 3D models demonstrate potential in accurately predicting ablation zones and optimizing MWA treatment strategies.
Keywords: 3D model; ablation zone; finite element method; image-guided cancer therapy; liver cancer; microwave ablation; necrotic tissue; thermal ablation.
Conflict of interest statement
Kristy K. Brock received grants from the National Institutes of Health and RaySearch Laboratories, holds a licensing agreement with RaySearch Laboratories, and is a member of RaySearch Laboratories’ advisory board. Bruno C. Odisio received research grants from Siemens Healthineers and Johnson & Johnson and consulting fees from Siemens Healthineers. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
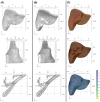

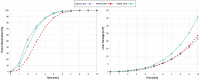

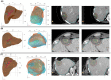
References
-
- Radosevic A., Quesada R., Serlavos C., Sánchez J., Zugazaga A., Sierra A., Coll S., Busto M., Aguilar G., Flores D., et al. Microwave versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of liver malignancies: A randomized controlled phase 2 trial. Sci. Rep. 2022;12:316. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03802-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vogl T.J., Martin S.S., Gruber-Rouh T., Booz C., Koch V., Nour-Eldin N.-E.A., Said M.N.H. RöFo-Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der Röntgenstrahlen und der Bildgebenden Verfahren. Volume 196. Georg Thieme Verlag KG; Leipzig, Germany: 2024. Comparison of Microwave and Radiofrequency Ablation for the Treatment of Small- and Medium-Sized Hepatocellular Carcinomas in a Prospective Randomized Trial; pp. 482–490. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

