Targeting Neoantigens in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38893220
- PMCID: PMC11171042
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16112101
Targeting Neoantigens in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
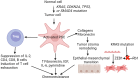
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the most common type of pancreatic cancer and is currently the third leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States after lung and colon cancer. PDAC is estimated to be the second leading cause of cancer-related death by 2030. The diagnosis at a late stage is the underlying cause for higher mortality and poor prognosis after surgery. Treatment resistance to chemotherapy and immunotherapy results in recurrence after surgery and poor prognosis. Neoantigen burden and CD8+ T-cell infiltration are associated with clinical outcomes in PDAC and paucity of neoantigen-reactive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes may be the underlying cause for treatment resistance for immunotherapy. This suggests a need to identify additional neoantigens and therapies targeting these neoantigens to improve clinical outcomes in PDAC. In this review, we focus on describing the pathophysiology, current treatment strategies, and treatment resistance in PDAC followed by the need to target neoantigens in PDAC.
Keywords: chemotherapy; immunotherapy; neoantigens; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; personalized therapy; targeted therapy; treatment resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. All the authors have read the manuscript and declare no conflicts of interest. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

