The Human Paraoxonase 2: An Optimized Procedure for Refolding and Stabilization Facilitates Enzyme Analyses and a Proteomics Approach
- PMID: 38893310
- PMCID: PMC11173892
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29112434
The Human Paraoxonase 2: An Optimized Procedure for Refolding and Stabilization Facilitates Enzyme Analyses and a Proteomics Approach
Abstract
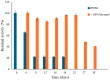
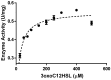
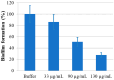
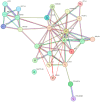
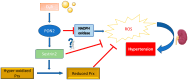
The human paraoxonase 2 (PON2) is the oldest member of a small family of arylesterase and lactonase enzymes, representing the first line of defense against bacterial infections and having a major role in ROS-associated diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegeneration, and diabetes. Specific Post-Translational Modifications (PTMs) clustering nearby two residues corresponding to pon2 polymorphic sites and their impact on the catalytic activity are not yet fully understood. Thus, the goal of the present study was to develop an improved PON2 purification protocol to obtain a higher amount of protein suitable for in-depth biochemical studies and biotechnological applications. To this end, we also tested several compounds to stabilize the active monomeric form of the enzyme. Storing the enzyme at 4 °C with 30 mM Threalose had the best impact on the activity, which was preserved for at least 30 days. The catalytic parameters against the substrate 3-Oxo-dodecanoyl-Homoserine Lactone (3oxoC12-HSL) and the enzyme ability to interfere with the biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PAO1) were determined, showing that the obtained enzyme is well suited for downstream applications. Finally, we used the purified rPON2 to detect, by the direct molecular fishing (DMF) method, new putative PON2 interactors from soluble extracts of HeLa cells.
Keywords: biofilm; enzyme kinetics; lactonase; paraoxonase; quorum quenching.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An Engineered Version of Human PON2 Opens the Way to Understand the Role of Its Post-Translational Modifications in Modulating Catalytic Activity.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 10;10(12):e0144579. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144579. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26656916 Free PMC article.
-
Dominant role of paraoxonases in inactivation of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing signal N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone.Infect Immun. 2008 Jun;76(6):2512-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01606-07. Epub 2008 Mar 17. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18347034 Free PMC article.
-
Paraoxonase 2 serves a proapopotic function in mouse and human cells in response to the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing molecule N-(3-Oxododecanoyl)-homoserine lactone.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 13;290(11):7247-58. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.620039. Epub 2015 Jan 27. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25627690 Free PMC article.
-
Human Paraoxonase-2 (PON2): Protein Functions and Modulation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 7;10(2):256. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020256. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33562328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Structure and Function of Paraoxonase-1 and Its Comparison to Paraoxonase-2 and -3.Molecules. 2020 Dec 17;25(24):5980. doi: 10.3390/molecules25245980. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33348669 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ng C.J., Wadleigh D.J., Gangopadhyay A., Hama S., Grijalva V.R., Navab M., Fogelman A.M., Reddy S.T. Paraoxonase-2 Is a Ubiquitously Expressed Protein with Antioxidant Properties and Is Capable of Preventing Cell-Mediated Oxidative Modification of Low Density Lipoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:44444–44449. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105660200. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

