Application of High-Z Nanoparticles to Enhance Current Radiotherapy Treatment
- PMID: 38893315
- PMCID: PMC11173748
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29112438
Application of High-Z Nanoparticles to Enhance Current Radiotherapy Treatment
Abstract
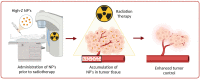
Radiotherapy is an essential component of the treatment regimens for many cancer patients. Despite recent technological advancements to improve dose delivery techniques, the dose escalation required to enhance tumor control is limited due to the inevitable toxicity to the surrounding healthy tissue. Therefore, the local enhancement of dosing in tumor sites can provide the necessary means to improve the treatment modality. In recent years, the emergence of nanotechnology has facilitated a unique opportunity to increase the efficacy of radiotherapy treatment. The application of high-atomic-number (Z) nanoparticles (NPs) can augment the effects of radiotherapy by increasing the sensitivity of cells to radiation. High-Z NPs can inherently act as radiosensitizers as well as serve as targeted delivery vehicles for radiosensitizing agents. In this work, the therapeutic benefits of high-Z NPs as radiosensitizers, such as their tumor-targeting capabilities and their mechanisms of sensitization, are discussed. Preclinical data supporting their application in radiotherapy treatment as well as the status of their clinical translation will be presented.
Keywords: cancer; chemotherapy; nanoparticle; radiosensitizer; radiotherapy; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Delivery of Nanoparticle-Based Radiosensitizers for Radiotherapy Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 31;21(1):273. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010273. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31906108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Radiosensitizers in Cancer Radiotherapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Feb 12;16:1083-1102. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S290438. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33603370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing X-Ray Sensitization with Multifunctional Nanoparticles.Small. 2024 Aug;20(35):e2400954. doi: 10.1002/smll.202400954. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Small. 2024. PMID: 38676336 Review.
-
Radiosensitizing high-Z metal nanoparticles for enhanced radiotherapy of glioblastoma multiforme.J Nanobiotechnology. 2020 Sep 3;18(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12951-020-00684-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020. PMID: 32883290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer Radiosensitizers.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Jan;39(1):24-48. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29224916 Review.
Cited by
-
Gold nanoparticle-loaded macrophages enhance radiotherapy via immune remodeling in oral cancer.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jun 27;33:102029. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102029. eCollection 2025 Aug. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40677404 Free PMC article.
-
An Anisotropic Gold-Palladium Heterostructured Nanosystem for Synergistically Overcoming Radioresistance and Enhancing Melanoma Radioimmunotherapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Aug;12(31):e00492. doi: 10.1002/advs.202500492. Epub 2025 Jun 17. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40525676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joiner M., van der Kogel A. Basic Clinical Radiobiology. 5th ed. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

