State of the Art in the Development of Human Serum Carnosinase Inhibitors
- PMID: 38893364
- PMCID: PMC11173852
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29112488
State of the Art in the Development of Human Serum Carnosinase Inhibitors
Abstract
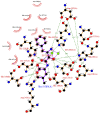
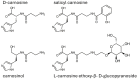
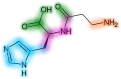
Human serum carnosinase is an enzyme that operates the preferential hydrolysis of dipeptides with a C-terminus histidine. Only higher primates excrete such an enzyme in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. In humans, the serum hydrolytic rate has high interindividual variability owing to gene polymorphism, although age, gender, diet, and also diseases and surgical interventions can modify serum activity. Human genetic diseases with altered carnosinase activity have been identified and associated with neurological disorders and age-related cognitive decline. On the contrary, low peripheral carnosinase activity has been associated with kidney protection, especially in diabetic nephropathy. Therefore, serum carnosinase is a druggable target for the development of selective inhibitors. However, only one molecule (i.e., carnostatine) has been discovered with the purpose of developing serum carnosinase inhibitors. Bestatin is the only inhibitor reported other than carnostatine, although its activity is not selective towards serum carnosinase. Herein, we present a review of the most critical findings on human serum carnosinase, including enzyme expression, localization and substrate selectivity, along with factors affecting the hydrolytic activity, its implication in human diseases and the properties of known inhibitors of the enzyme.
Keywords: bestatin; carnosine; carnostatine; inhibitors; serum carnosinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
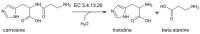
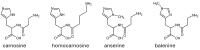
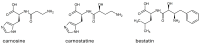
Similar articles
-
Separation and characterization of two carnosine-splitting cytosolic dipeptidases from hog kidney (carnosinase and non-specific dipeptidase).Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990 May;371(5):433-40. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1990.371.1.433. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990. PMID: 2378680
-
Characterization of human tissue carnosinase.Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):653-60. doi: 10.1042/bj2280653. Biochem J. 1985. PMID: 4026801 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterisation of carnostatine (SAN9812), a potent and selective carnosinase (CN1) inhibitor with in vivo activity.Amino Acids. 2019 Jan;51(1):7-16. doi: 10.1007/s00726-018-2601-z. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Amino Acids. 2019. PMID: 29922921
-
[Carnosine, carnosinase and kidney diseases].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012 Apr 20;66:215-21. doi: 10.5604/17322693.991600. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012. PMID: 22706107 Review. Polish.
-
Carnosinases, their substrates and diseases.Molecules. 2014 Feb 21;19(2):2299-329. doi: 10.3390/molecules19022299. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24566305 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anserine, Balenine, and Ergothioneine: Impact of Histidine-Containing Compounds on Exercise Performance-A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 27;17(5):828. doi: 10.3390/nu17050828. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40077698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Why Bestatin Prefers Human Carnosinase 2 (CN2) to Human Carnosinase 1 (CN1).J Phys Chem B. 2024 Dec 5;128(48):11876-11884. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.4c05571. Epub 2024 Nov 22. J Phys Chem B. 2024. PMID: 39574306 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Secondary Amine Carnosine Derivatives: Design, Synthesis, and Properties.Molecules. 2024 Oct 28;29(21):5083. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215083. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519724 Free PMC article.
-
Low Plasma Carnosinase-1 Activity in Patients with Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction: Implications for Carnosine Therapy in Heart Failure.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 14;26(6):2608. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062608. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murphey W.H., Patchen L., Lindmark D.G. Carnosinase: A fluorometric assay and demonstration of two electrophoretic forms in human tissue extracts. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1972;42:309–314. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90094-0. - DOI
-
- Teufel M., Saudek V., Ledig J.P., Bernhardt A., Boularand S., Carreau A., Cairns N.J., Carter C., Cowley D.J., Duverger D., et al. Sequence identification and characterization of human carnosinase and a closely related non-specific dipeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:6521–6531. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209764200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

