Baicalin and Baicalein Enhance Cytotoxicity, Proapoptotic Activity, and Genotoxicity of Doxorubicin and Docetaxel in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 38893380
- PMCID: PMC11173533
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29112503
Baicalin and Baicalein Enhance Cytotoxicity, Proapoptotic Activity, and Genotoxicity of Doxorubicin and Docetaxel in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
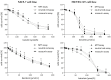
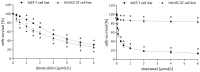
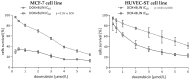
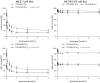
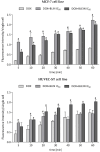
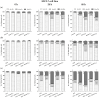
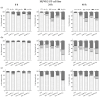
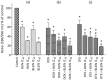
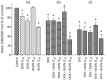
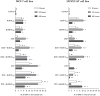
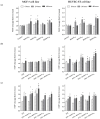
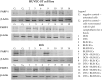
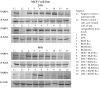
Breast cancer is a major health concern and the leading cause of death among women worldwide. Standard treatment often involves surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy, but these come with side effects and limitations. Researchers are exploring natural compounds like baicalin and baicalein, derived from the Scutellaria baicalensis plant, as potential complementary therapies. This study investigated the effects of baicalin and baicalein on the cytotoxic, proapoptotic, and genotoxic activity of doxorubicin and docetaxel, commonly used chemotherapeutic drugs for breast cancer. The analysis included breast cancer cells (MCF-7) and human endothelial cells (HUVEC-ST), to assess potential effects on healthy tissues. We have found that baicalin and baicalein demonstrated cytotoxicity towards both cell lines, with more potent effects observed in baicalein. Both flavonoids, baicalin (167 µmol/L) and baicalein (95 µmol/L), synergistically enhanced the cytotoxic, proapoptotic, and genotoxic activity of doxorubicin and docetaxel in breast cancer cells. In comparison, their effects on endothelial cells were mixed and depended on concentration and time. The results suggest that baicalin and baicalein might be promising complementary agents to improve the efficacy of doxorubicin and docetaxel anticancer activity. However, further research is needed to validate their safety and efficacy in clinical trials.
Keywords: DNA damage; apoptosis; baicalein; baicalin; cytotoxicity; docetaxel; doxorubicin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Back N., Cohen I.R., Lajtha A., Lambris J.D., Paoletti R., Yu D., Hung M.-C. Breast Cancer Chemosensitivity. Scholars Portal; New York, NY, USA: 2007.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

