A Convenient In Situ Preparation of Cu2ZnSnS4-Anatase Hybrid Nanocomposite for Photocatalysis/Photoelectrochemical Water-Splitting Hydrogen Production
- PMID: 38893390
- PMCID: PMC11173519
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29112514
A Convenient In Situ Preparation of Cu2ZnSnS4-Anatase Hybrid Nanocomposite for Photocatalysis/Photoelectrochemical Water-Splitting Hydrogen Production
Abstract
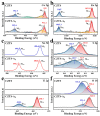
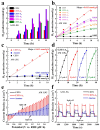
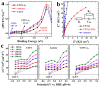
This study details the rational design and synthesis of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS)-doped anatase (A) heterostructures, utilizing earth-abundant elements to enhance the efficiency of solar-driven water splitting. A one-step hydrothermal method was employed to fabricate a series of CZTS-A heterojunctions. As the concentration of titanium dioxide (TiO2) varied, the morphology of CZTS shifted from floral patterns to sheet-like structures. The resulting CZTS-A heterostructures underwent comprehensive characterization through photoelectrochemical response assessments, optical measurements, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analyses. Detailed photoelectrochemical (PEC) investigations demonstrated notable enhancements in photocurrent density and incident photon-to-electron conversion efficiency (IPCE). Compared to pure anatase electrodes, the optimized CZTS-A heterostructures exhibited a seven-fold increase in photocurrent density and reached a hydrogen production efficiency of 1.1%. Additionally, the maximum H2 production rate from these heterostructures was 11-times greater than that of pure anatase and 250-times higher than the original CZTS after 2 h of irradiation. These results underscore the enhanced PEC performance of CZTS-A heterostructures, highlighting their potential as highly efficient materials for solar water splitting. Integrating Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoparticles (NPs) within TiO2 (anatase) heterostructures implied new avenues for developing earth-abundant and cost-effective photocatalytic systems for renewable energy applications.
Keywords: Cu2ZnSnS4–anatase nanocomposite; copper-based sulfides; heterojunction; photocatalytic H2 generation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Yokoyama D., Minegishi T., Jimbo K., Hisatomi T., Ma G., Katayama M., Kubota J., Katagiri H., Domen K. H2 Evolution from Water on Modified Cu2ZnSnS4 Photoelectrode under Solar Light. Appl. Phys. Express. 2010;3:101202. doi: 10.1143/apex.3.101202. - DOI
-
- Hisatomi T., Minegishi T., Domen K. Kinetic Assessment and Numerical Modeling of Photocatalytic Water Splitting toward Efficient Solar Hydrogen Production. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2012;85:647–655. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.20120058. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 22275185/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023H0046/Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province
- 3502Z20191015/Major Research Project of Xiamen
- 2021ZR132/Fujian Science & Technology Innovation Laboratory for Optoelectronic Information of China
- 2021ZZ115/Fujian Science & Technology Innovation Laboratory for Optoelectronic Information of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

