O-Phthalaldehyde Derivatization for the Paper-Based Fluorometric Determination of Glutathione in Nutritional Supplements
- PMID: 38893425
- PMCID: PMC11173998
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29112550
O-Phthalaldehyde Derivatization for the Paper-Based Fluorometric Determination of Glutathione in Nutritional Supplements
Abstract
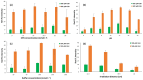
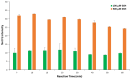
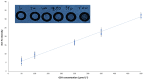
Herein, a new, direct paper-based fluorimetric method is described for the quantitative determination of glutathione (GSH) molecules in nutritional supplements. Briefly, the proposed analytical method is based on the fluorescence emission resulting from the direct and selective chemical reaction of GSH molecules with the derivatization reagent that is o-phthalaldehyde (OPA) in acidic conditions at room temperature. The intensity of the emitted fluorescence on the surface of the analytical paper devices after irradiation with a lamp at 365 nm is proportional to the concentration of GSH and is measured using a smartphone as the detector. This methodology, which is suitable for measurements in laboratories with limited resources, does not require specialized instrumentation or trained personnel. The protocol governing the proposed method is simple and easily applicable. Essentially, the chemical analyst should adjust the value of pH on the surface of the paper by adding a minimal amount of buffer solution; then, after adding a few microliters of the derivatization reagent, wait for the surface of the paper to dry and, finally, add the analyte. Subsequently, the irradiation of the sensor and the measurement of the emitted fluorescence can be recorded with a mobile phone. In the present study, several parameters affecting the chemical reaction and the emitted fluorescence were optimized, the effect of interfering compounds that may be present in dietary supplements was examined, and the stability of these paper sensors under different storage conditions was evaluated. Additionally, the chemical stability of these paper devices in various maintenance conditions was studied, with satisfactory results. The detection limit calculated as 3.3 S/N was 20.5 μmol L-1, while the precision of the method was satisfactory, ranging from 3.1% (intra-day) to 7.3% (inter-day). Finally, the method was successfully applied to three different samples of dietary supplements.
Keywords: UV irradiation; fluorimetric determination; glutathione; nutritional supplement formulations; paper-based analytical devices.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kanďár R., Vrbová M., Čandová J. An assay of total glutathione and glutathione disulfide in human whole blood and plasma using a high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat Technol. 2013;36:2013–2028. doi: 10.1080/10826076.2012.706858. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

