The Dependence of Hydrophobic Interactions on the Shape of Solute Surface
- PMID: 38893477
- PMCID: PMC11173737
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29112601
The Dependence of Hydrophobic Interactions on the Shape of Solute Surface
Abstract
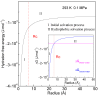
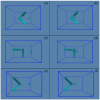
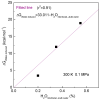
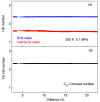
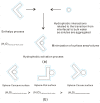
According to our recent studies on hydrophobicity, this work is aimed at understanding the dependence of hydrophobic interactions on the shape of a solute's surface. It has been observed that dissolved solutes primarily affect the structure of interfacial water, which refers to the top layer of water at the interface between the solute and water. As solutes aggregate in a solution, hydrophobic interactions become closely related to the transition of water molecules from the interfacial region to the bulk water. It is inferred that hydrophobic interactions may depend on the shape of the solute surface. To enhance the strength of hydrophobic interactions, the solutes tend to aggregate, thereby minimizing their surface area-to-volume ratio. This also suggests that hydrophobic interactions may exhibit directional characteristics. Moreover, this phenomenon can be supported by calculated potential mean forces (PMFs) using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, where different surfaces, such as convex, flat, or concave, are associated with a sphere. Furthermore, this concept can be extended to comprehend the molecular packing parameter, commonly utilized in studying the self-assembly behavior of amphiphilic molecules in aqueous solutions.
Keywords: hydrogen bonding; hydrophobic interactions; solute shape; water.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Israelachvili J.N., Mitchell D.J., Ninham B.W. Theory of self-assembly of hydrocarbon amphiphiles into micelles and bilayers. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1976;72:1525–1568. doi: 10.1039/f29767201525. - DOI
-
- Nagarajan R. Molecular packing parameter and surfactant self-assembly: The neglected role of the surfactant tail. Langmuir. 2002;18:31–38. doi: 10.1021/la010831y. - DOI
-
- Frank H.S., Evans M.W. Free volume and entropy in condensed systems III. Entropy in binary liquid mixtures; partial molal entropy in dilute solutions; structure and thermodynamics in aqueous electrolytes. J. Chem. Phys. 1945;13:507–532. doi: 10.1063/1.1723985. - DOI
-
- Stillinger F.H. Structure in aqueous solutions of nonpolar solutes from the standpoint of scaled-particle theory. J. Solution Chem. 1973;2:141–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00651970. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

