Apigenin's Modulation of Doxorubicin Efficacy in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 38893482
- PMCID: PMC11174085
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29112603
Apigenin's Modulation of Doxorubicin Efficacy in Breast Cancer
Abstract
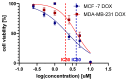
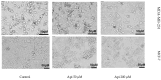
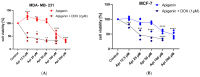
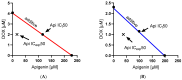
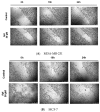
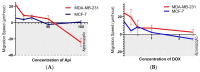
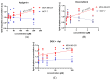
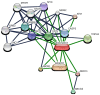
Apigenin, a naturally derived flavonoid, is increasingly being acknowledged for its potential therapeutic applications, especially in oncology. This research explores apigenin's capacity to modulate cancer cell viability, emphasizing its roles beyond its minimal antioxidant activity attributed to its basic molecular structure devoid of hydroxyl groups. We investigated apigenin's effects on two breast cancer cell lines, estrogen-dependent MCF-7 and non-estrogen-dependent MDA-MB-231 cells. Our findings reveal that apigenin exerts a dose-dependent cytotoxic and anti-migratory impact on these cells. Interestingly, both apigenin and doxorubicin-a standard chemotherapeutic agent-induced lipid droplet accumulation in a dose-dependent manner in MDA-MB-231 cells. This phenomenon was absent in MCF-7 cells and not evident when doxorubicin and apigenin were used concurrently, suggesting distinct cellular responses to these treatments that imply that their synergistic effects might be mediated through mechanisms unrelated to lipid metabolism. A further chemoinformatics analysis indicated that apigenin and doxorubicin might interact primarily at the level of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter proteins, with potential indirect influences from the AKT and MYC signaling pathways. These results highlight the importance of understanding the nuanced interactions between apigenin and conventional chemotherapeutic drugs, as they could lead to more effective strategies for cancer treatment. This study underscores apigenin's potential as a modulator of cancer cell dynamics through mechanisms independent of its direct antioxidant effects, thereby contributing to the development of flavonoid-based adjunct therapies in cancer management.
Keywords: anticancer; breast cancer treatment; flavonoids; nutrition; synergistic effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ashrafizadeh M., Bakhoda M.R., Bahmanpour Z., Ilkhani K., Zarrabi A., Makvandi P., Khan H., Mazaheri S., Darvish M., Mirzaei H. Apigenin as Tumor Suppressor in Cancers: Biotherapeutic Activity, Nanodelivery, and Mechanisms With Emphasis on Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Chem. 2020;8:829. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00829. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mushtaq Z., Sadeer N.B., Hussain M., Mahwish, Alsagaby S.A., Imran M., Mumtaz T., Umar M., Tauseef A., Al Abdulmonem W., et al. Therapeutical Properties of Apigenin: A Review on the Experimental Evidence and Basic Mechanisms. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023;26:1914–1939. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2023.2236329. - DOI
-
- Pogorzelska A., Mazur M., Świtalska M., Wietrzyk J., Sigorski D., Fronczyk K., Wiktorska K. Anticancer Effect and Safety of Doxorubicin and Nutraceutical Sulforaphane Liposomal Formulation in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Animal Model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023;161:114490. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114490. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

