Optimization of Flavonoid Extraction from Abelmoschus manihot Flowers Using Ultrasonic Techniques: Predictive Modeling through Response Surface Methodology and Deep Neural Network and Biological Activity Assessment
- PMID: 38893486
- PMCID: PMC11173679
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29112610
Optimization of Flavonoid Extraction from Abelmoschus manihot Flowers Using Ultrasonic Techniques: Predictive Modeling through Response Surface Methodology and Deep Neural Network and Biological Activity Assessment
Abstract
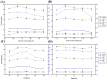
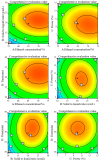
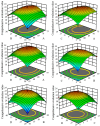
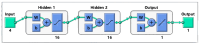
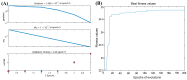
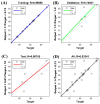
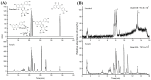
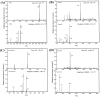
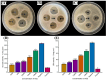
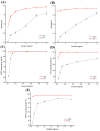
Understanding the optimal extraction methods for flavonoids from Abelmoschus manihot flowers (AMF) is crucial for unlocking their potential benefits. This study aimed to optimize the efficiency of flavonoid extraction from AMF. After comparing extraction methods, the ultrasonic cell crusher demonstrated superior performance over conventional techniques. Four key factors-solid-to-liquid ratio (1:10 to 1:50 g·mL-1), ethanol concentration (55% to 95%), ultrasonic time (10 to 50 min), and ultrasonic power (5% to 25% of 900 W)-were investigated and normalized using the entropy weight method. This led to a comprehensive evaluation (CE). Optimization of extraction conditions for the ultrasonic cell crusher was achieved through response surface methodology and a deep neural network model, resulting in optimal parameters: ethanol volume fraction of 66%, solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:21 g/mL, extraction efficiency of 9%, and extraction duration of 35 min, yielding a CE value of 23.14 (RSD < 1%). Additionally, the inhibitory effects of the optimized extracts against Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans) were assessed. The results revealed that AMF extract (AMFE) exhibits inhibitory effects on S. mutans, with concomitant inhibition of sucrase and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). The MIC of AMFE against planktonic S. mutans is 3 mg/mL, with an MBC of 6 mg/mL. Within the concentration range of 1/8 MIC to 2 MIC of AMFE, the activities of sucrase and LDH decreased by 318.934 U/mg prot and 61.844 U/mg prot, respectively. The antioxidant activity of AMFE was assessed using the potassium ferricyanide reduction and phosphomolybdenum methods. Additionally, the effect of AMFE on DPPH, ABTS, and ·OH free radical scavenging abilities was determined. The concentrations at which AMFE exhibited over 90% scavenging rate for ABTS and DPPH free radicals were found to be 0.125 mg/mL and 2 mg/mL, respectively.
Keywords: Abelmoschus manihot flower; Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans); antioxidant activity; dental caries; green extraction; ultrasonic cell crusher.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Li Y., Ge Z.H., Duan Q.H., Yu S.L., Li Y.J., Tan X.Y., Wang D. Content Determination of Active Constituents in Abelmoschi Corolla. Asia-Pac. Tradit. Med. 2014;10:16–18.
-
- Ge J., Miao J.J., Sun X.Y., Yu J.Y. Huangkui capsule, an extract from Abelmoschus manihot (L.) medic, improves diabetic nephropathy via activating peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor (PPAR)-α/γ and attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016;189:238–249. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.033. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jain P.S., Bari S.B. Anti-inflammatory Activity of Abelmoschus manihot Extracts. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2010;6:505–509. doi: 10.3923/ijp.2010.505.509. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

