Green Method Comparison and Optimization of Anthocyanin Recovery from "Sangiovese" Grape Pomace: A Critical Evaluation of the Design of Experiments Approach
- PMID: 38893553
- PMCID: PMC11173428
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29112679
Green Method Comparison and Optimization of Anthocyanin Recovery from "Sangiovese" Grape Pomace: A Critical Evaluation of the Design of Experiments Approach
Abstract
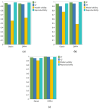
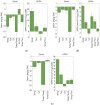
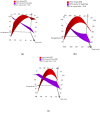
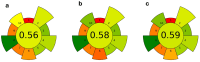
Grape pomace is the main by-product obtained from wine production that is still enriched in bioactive compounds. Within a framework of waste/by-product reuse through a sustainable approach, various green methods were utilized in this work to recover anthocyanins from the pomace resulting from "Sangiovese" grape vinification. Ultrasound- and Microwave-Assisted Extractions (UAE and MAE) were coupled with the use of green solvents, such as acidified water, an ethanol/water mixture, and Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NaDES), and their efficacy was compared with that of a conventional method based on a methanol/acidified water mixture. The Total Anthocyanin Index ranged from 36.9 to 75.2 mg/g DW for UAE, and from 54.4 to 99.6 mg/g DW for MAE, while resulting in 47.1 mg/g DW for conventional extraction. A Design of Experiments (DoE) approach was applied to MAE, the most efficient technique. Temperature, time, and the solid-to-liquid ratio were set as X variables, while malvidin-3-O-glucoside content and antioxidant activity were used as response variables, measured by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array Detection (HPLC-DAD) and 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay, respectively. The correlation between temperature and time and the antioxidant activity of the extract was positive, while it was found to be negative when considering malvidin-3-O-glucoside concentration as a response variable. Thus, the optimal conditions in temperature, time and solid-to-liquid ratio were different depending on the chosen variable. The results underline the importance of selecting an accurate response when using the response surface methodology approach.
Keywords: Design of Experiments; MAE; MODDE; NaDES; UAE; anthocyanins; grape pomace; green extraction; response surface model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- European Commission . Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions. Volume 667 European Commission; Brussels, Belgium: 2020. Chemicals Strategy for Sustainability towards a Toxic-Free Environment.
-
- Chemat F., Abert-Vian M., Fabiano-Tixier A.S., Strube J., Uhlenbrock L., Gunjevic V., Cravotto G. Green Extraction of Natural Products. Origins, Current Status, and Future Challenges. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019;118:248–263. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2019.05.037. - DOI
-
- Chemat F., Vian M.A., Fabiano-Tixier A.-S., Nutrizio M., Jambrak A.R., Munekata P.E.S., Lorenzo J.M., Barba F.J., Binello A., Cravotto G. A Review of Sustainable and Intensified Techniques for Extraction of Food and Natural Products. Green Chem. 2020;22:2325–2353. doi: 10.1039/C9GC03878G. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

