Artificial Intelligence in Point-of-Care Biosensing: Challenges and Opportunities
- PMID: 38893627
- PMCID: PMC11172335
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14111100
Artificial Intelligence in Point-of-Care Biosensing: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
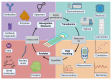
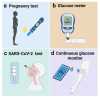
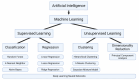
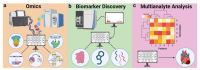
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into point-of-care (POC) biosensing has the potential to revolutionize diagnostic methodologies by offering rapid, accurate, and accessible health assessment directly at the patient level. This review paper explores the transformative impact of AI technologies on POC biosensing, emphasizing recent computational advancements, ongoing challenges, and future prospects in the field. We provide an overview of core biosensing technologies and their use at the POC, highlighting ongoing issues and challenges that may be solved with AI. We follow with an overview of AI methodologies that can be applied to biosensing, including machine learning algorithms, neural networks, and data processing frameworks that facilitate real-time analytical decision-making. We explore the applications of AI at each stage of the biosensor development process, highlighting the diverse opportunities beyond simple data analysis procedures. We include a thorough analysis of outstanding challenges in the field of AI-assisted biosensing, focusing on the technical and ethical challenges regarding the widespread adoption of these technologies, such as data security, algorithmic bias, and regulatory compliance. Through this review, we aim to emphasize the role of AI in advancing POC biosensing and inform researchers, clinicians, and policymakers about the potential of these technologies in reshaping global healthcare landscapes.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; biosensor; machine learning; point-of-care.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Advancing Biosensor Technology: Past, Present, and Future Perspectives.Adv Mater. 2025 Jun 16:e2504796. doi: 10.1002/adma.202504796. Online ahead of print. Adv Mater. 2025. PMID: 40522091 Review.
-
Assuring assistance to healthcare and medicine: Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, and Artificial Intelligence of Things.Front Artif Intell. 2024 Dec 13;7:1442254. doi: 10.3389/frai.2024.1442254. eCollection 2024. Front Artif Intell. 2024. PMID: 39735232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Partnering With Technology: Advancing Laparoscopy With Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.Cureus. 2024 Mar 13;16(3):e56076. doi: 10.7759/cureus.56076. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38618354 Free PMC article.
-
AI-driven healthcare: Fairness in AI healthcare: A survey.PLOS Digit Health. 2025 May 20;4(5):e0000864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000864. eCollection 2025 May. PLOS Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40392801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smart Smile: Revolutionizing Dentistry With Artificial Intelligence.Cureus. 2023 Jun 30;15(6):e41227. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41227. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37529520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in cell-based biosensors: Transforming food flavor evaluation with novel approaches.Food Chem X. 2025 Mar 1;26:102336. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102336. eCollection 2025 Feb. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40115496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in machine learning-enhanced nanozymes.Front Chem. 2024 Oct 17;12:1483986. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1483986. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 39483853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hardware-Assisted Low-Latency NPU Virtualization Method for Multi-Sensor AI Systems.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Dec 15;24(24):8012. doi: 10.3390/s24248012. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39771750 Free PMC article.
-
Fundamentals and research progression on electrochemical sensing of colorectal cancer.Mikrochim Acta. 2025 May 14;192(6):355. doi: 10.1007/s00604-025-07207-9. Mikrochim Acta. 2025. PMID: 40369291 Review.
-
Advancing clinical biochemistry: addressing gaps and driving future innovations.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 8;12:1521126. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1521126. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40265187 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

