Aging of Superficial Musculoaponeurotic System of the Face-Novel Biomarkers and Micro-CT Relevance of Facial Anti-Gravity Support
- PMID: 38893653
- PMCID: PMC11172020
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14111126
Aging of Superficial Musculoaponeurotic System of the Face-Novel Biomarkers and Micro-CT Relevance of Facial Anti-Gravity Support
Abstract
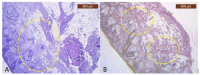
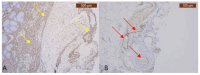
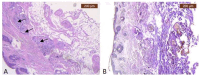
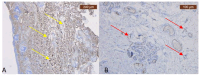
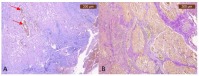
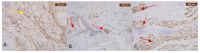
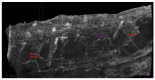
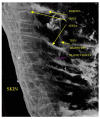
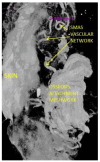
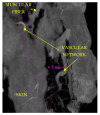
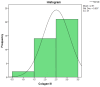
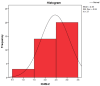
The soft superficial tissues of the face are against gravity through an intricate network of ligaments and ligamentous attachments. The aim of this investigation is to delineate the relationship between the muscular, fibrous, and vascular components of the superficial musculoaponeurotic system of the face (SMAS) at the level of its periosteal fixation areas from advanced radiological and novel biomarkers' perspectives. These areas represent key points underlying skin aging and the longevity of restorative surgery results. Methods: This study was carried out on 37 surgical specimens, excised from patients admitted for surgery. On the excised specimens, we used special immunohistochemical techniques, such as markers for collagen type III, angiogenesis, vascular endothelium (I-CAM2) and muscle fibers (MYH2). We performed a micro-CT evaluation of these 37 specimens. Results: The results of this study showed different radiologic and IHC characteristics of the means of periosteal fixation of the SMAS. Evidence of morphohistological and radiological peculiarities of the retaining ligaments highlights new data for future functional studies of these structures. Our research must be continued with larger groups of subjects and through detailed methodological studies of vascular microperfusion and could represent an important new step in biotissue engineering and the customization of surgical techniques involving the sub-SMAS layers.
Keywords: SMAS; aging biomarkers; anti-aging; facial ligaments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



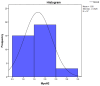
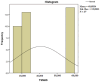
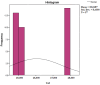
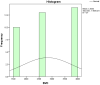
References
-
- Sahin O.S., Hanalioglu S., Metin Sanli A., Bakir A., Comert A., Baskaya M.K. Angiographic measurement of the superficial temporal artery for potential use in cerebral bypass surgery: A combined radiological and cadaveric study. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2024;46:605–614. doi: 10.1007/s00276-024-03325-w. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

