Image-Guided Minimally Invasive Treatment Options for Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease: A Practical Overview of Current Possibilities
- PMID: 38893672
- PMCID: PMC11171713
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14111147
Image-Guided Minimally Invasive Treatment Options for Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease: A Practical Overview of Current Possibilities
Abstract
Lumbar back pain is one of the main causes of disability around the world. Most patients will complain of back pain at least once in their lifetime. The degenerative spine is considered the main cause and is extremely common in the elderly population. Consequently, treatment-related costs are a major burden to the healthcare system in developed and undeveloped countries. After the failure of conservative treatments or to avoid daily chronic drug intake, invasive treatments should be suggested. In a world where many patients reject surgery and prefer minimally invasive procedures, interventional radiology is pivotal in pain management and could represent a bridge between medical therapy and surgical treatment. We herein report the different image-guided procedures that can be used to manage degenerative spine-related low back pain. Particularly, we will focus on indications, different techniques, and treatment outcomes reported in the literature. This literature review focuses on the different minimally invasive percutaneous treatments currently available, underlining the central role of radiologists having the capability to use high-end imaging technology for diagnosis and subsequent treatment, allowing a global approach, reducing unnecessary surgeries and prolonged pain-reliever drug intake with their consequent related complications, improving patients' quality of life, and reducing the economic burden.
Keywords: interventional radiology; interventional ultrasonography; intervertebral disc degeneration; low back pain; lumbar osteoarthritis; magnetic resonance imaging; multidetector computed tomography; pain management; pulsed radiofrequency treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






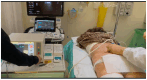
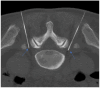
References
-
- Vos T., Barber R.M., Bell B., Bertozzi-Villa A., Biryukov S., Bolliger I., Charlson F., Davis A., Degenhardt L., Dicker D., et al. Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 301 Acute and Chronic Diseases and Injuries in 188 Countries, 1990–2013: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386:743–800. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

