Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Sampling for the Cytohistological Diagnosis of Focal Liver Lesions
- PMID: 38893681
- PMCID: PMC11171570
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14111155
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Sampling for the Cytohistological Diagnosis of Focal Liver Lesions
Abstract
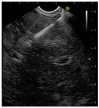
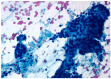
Background: Focal liver lesions (FLL) often require cytohistological evaluation. Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)-guided tissue acquisition (EUS-TA) is highly accurate in diagnosing pancreatic and gastrointestinal malignancies. The aim of our study was to evaluate the role of EUS-TA in the characterization of FLL.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of a prospective database of patients who underwent EUS-TA for the evaluation of FLL. Diagnostic yield, adverse events and factors associated with diagnostic yield were evaluated as endpoints. The effect of variables such as needle size, lesion size, rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) and the use of cytological or histological needles were analyzed.
Results: A total of 114 cases were included (mean age 68.05 ± 11.35 years, 64 male). A correct diagnosis was made using EUS-TA in 100 of the 114 cases (diagnostic yield of 88%). The EUS-TA of additional extrahepatic lesions during the same EUS procedure increased the diagnostic yield to 94%. No adverse events were reported. Multivariate analysis did not identify any factor influencing the diagnostic yield.
Conclusions: EUS-TA is a highly accurate and safe technique for the differential diagnosis of FLL and could be considered as the primary approach in this setting.
Keywords: diagnostic yield; endoscopic ultrasound; focal liver lesions.
Conflict of interest statement
José Lariño-Noia, Julio Iglesias-Garcia and Juan Enrique Dominguez-Muñoz have received honoraria as speakers from Boston Scientifc, Pentax, Abbot and Viatris. Daniel de la Iglesia-García has received honoraria as speaker from Abbot and Viatris. Andrea Jardí, Marco Galego, Alberto Rama, Xurxo Martínez, Yessica Dominguez and Ihab Abdulkader have not potential conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition with or without rapid on-site evaluation for solid pancreatic lesions: five years of experience from a single center.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul-Dec;58(10):1185-1193. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2023.2204985. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37114616
-
Diagnostic yield of endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition of solid pancreatic lesions after inconclusive percutaneous ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2020 Sep;55(9):1108-1113. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2020.1794021. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32684051
-
Diagnostic performance of endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition by EUS-FNA versus EUS-FNB for solid pancreatic mass without ROSE: a retrospective study.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Jun 24;20(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02682-3. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35751053 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic ultrasound core needle for diagnosing of solid pancreatic lesions: is rapid on-site evaluation really necessary?Minerva Med. 2017 Dec;108(6):547-553. doi: 10.23736/S0026-4806.17.05327-7. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Minerva Med. 2017. PMID: 28750500 Review.
-
Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided tissue acquisition for small solid pancreatic lesions: Does the size matter?DEN Open. 2021 Sep 28;2(1):e52. doi: 10.1002/deo2.52. eCollection 2022 Apr. DEN Open. 2021. PMID: 35310760 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The outcomes of endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition for small focal liver lesions measuring ≤2 cm.DEN Open. 2024 Oct 21;5(1):e70031. doi: 10.1002/deo2.70031. eCollection 2025 Apr. DEN Open. 2024. PMID: 39439546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elsayes K.M., Ellis J.H., Elkhouly T., Ream J.M., Bowerson M., Khan A., Caoili E.M. Diagnostic yield of percutaneous image-guided tissue biopsy of focal hepatic lesions in cancer patients: Ten percent are not metastases from primary malignancy. Cancer. 2011;117:4041–4048. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25980. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buscarini L., Fornari F., Bolondi L., Colombo P., Livraghi T., Magnolfi F., Rapaccini G.L., Salmi A. Ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsy of focal liver lesions: Techniques, diagnostic accuracy, and complications. A retrospective study on 2091 biopsies. J. Hepatol. 1990;11:344–348. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(90)90219-H. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

