Frozen Section of Placental Membranes and Umbilical Cord: A Valid Diagnostic Tool for Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis Management
- PMID: 38893683
- PMCID: PMC11171626
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14111157
Frozen Section of Placental Membranes and Umbilical Cord: A Valid Diagnostic Tool for Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis Management
Abstract
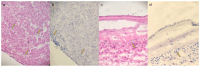
Early-onset neonatal sepsis (EONS), a serious infection in newborns within 3 days, is challenging to diagnose. The current methods often lack accuracy, leading to unnecessary antibiotics or delayed treatment. This study investigates the role of the frozen section examination of placental membranes and umbilical cord (FSMU) to improve EONS diagnosis in the daily lab practice. This retrospective study reviewed data from 59 neonates with EONS risk factors who underwent FSMU according to our institutional protocol. Concordance between the FSMU and the Final Pathological Report (FPR) was assessed. The FSMU demonstrated a high concordance (Kappa = 0.88) for funisitis diagnosis, with excellent accuracy (98.3%). A moderate concordance was observed for chorioamnionitis stage and grade. The FSMU shows promise as a rapid and accurate tool for diagnosing EONS, particularly for funisitis. This study suggests that the FSMU could be a valuable tool for EONS diagnosis, enabling a more judicious antibiotic use and potentially improving outcomes for newborns.
Keywords: chorioamnionitis; frozen section examination; funisitis; neonatal sepsis; placenta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- MSD Manuals Neonatal Sepsis. [(accessed on 15 February 2024)]. Available online: https://www.merckmanuals.com/en-pr/professional/pediatrics/infections-in....
-
- National Institutes of Health Neonatal Sepsis. [(accessed on 15 February 2024)]; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531478.
-
- Araújo B.C., Guimarães H. Risk factors for neonatal sepsis: An overview. J. Pediatr. Neonatal Individ. Med. 2020;9:e090206.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

