Patient-Reported Outcome Measures in Patients with and without Non-Expandable Lung Secondary to Malignant Pleural Effusion-A Single-Centre Observational Study
- PMID: 38893702
- PMCID: PMC11171895
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14111176
Patient-Reported Outcome Measures in Patients with and without Non-Expandable Lung Secondary to Malignant Pleural Effusion-A Single-Centre Observational Study
Abstract
Background: Malignant pleural effusion (MPE) affects up to 15% of patients with malignancy, and the prevalence is increasing. Non-expandable lung (NEL) complicates MPE in up to 30% of cases. However, it is not known if patients with malignant pleural effusion and NEL are more symptomatic in activities of daily living compared to patients with MPE with expandable lung.
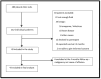
Methods: This was an observational study on consecutively recruited patients with MPE from our pleural clinic. Before thoracentesis, patients completed patient-reported outcomes on cancer symptoms (ESAS), health-related quality of life (5Q-5D-5L), and dyspnoea scores. Following thoracentesis, patients scored dyspnoea relief and symptoms during thoracentesis. Data on focused lung ultrasound and pleural effusion biochemistry were collected. The non-expandable lung diagnosis was made by pleural experts based on radiological and clinical information.
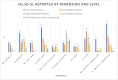
Results: We recruited 43 patients, including 12 with NEL (28%). The NEL cohort resembled those from previous studies concerning ultrasonography, pleural fluid biochemistry, and fewer cases with high volume thoracentesis. Patients with and without NEL were comparable concerning baseline demography. The 5Q-5D-5L utility scores were 0.836 (0.691-0.906) and 0.806 (0.409-0.866), respectively, for patients with and without NEL. We observed no between-group differences in symptom burden or health-related quality of life.
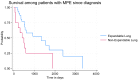
Conclusion: While the presence of NEL affects the clinical management of recurrent MPE, the presence of NEL seems not to affect patients' overall symptom burden in patients with MPE.
Keywords: malignant pleural effusion; non-expandable lung; patient-reported outcomes; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Bodtger U., Hallifax R.J. Pleural Diseases ERS Monograph. ERS; Sheffield, UK: 2020. Epidemiology: Why is pleural disease becoming more common?
-
- Dresler C.M., Olak J., Herndon J.E., Richards W.G., Scalzetti E., Fleishman S.B., Kernstine K.H., Demmy T., Jablons D.M., Kohman L., et al. Phase III Intergroup Study of Talc Poudrage vs. Talc Slurry Sclerosis for Malignant Pleural Effusion. Chest. 2005;127:909–915. doi: 10.1378/chest.127.3.909. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources