CaAl-Layered Double Hydroxides-Modified Biochar Composites Mitigate the Toxic Effects of Cu and Pb in Soil on Pea Seedlings
- PMID: 38894027
- PMCID: PMC11173730
- DOI: 10.3390/ma17112763
CaAl-Layered Double Hydroxides-Modified Biochar Composites Mitigate the Toxic Effects of Cu and Pb in Soil on Pea Seedlings
Abstract
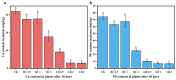
Compound contamination of soil with heavy metals copper (Cu) and lead (Pb) triggered by mining development has become a serious problem. To solve this problem, in this paper, corncob kernel, which is widely available and inexpensive, was used as the raw material of biochar and modified by loading CaAl-layered double hydroxides to synthesize biochar-loaded CaAl-layered double hydroxide composites (CaAl-LDH/BC). After soil remediation experiments, either BC or CaAl-LDH/BC can increase soil pH, and the available phosphorus content and available potassium content in soil. Compared with BC, CaAl-LDH/BC significantly reduced the available content of Cu and Pb in the active state (diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid extractable state) in the soil, and the passivation rate of Cu and Pb by a 2% dosage of CaAl-LDH/BC reached 47.85% and 37.9%, respectively. CaAl-LDH/BC can significantly enhance the relative abundance of beneficial microorganisms such as Actinobacteriota, Gemmatimonadota, and Luteimonas in the soil, which can help to enhance the tolerance and reduce the enrichment ability of plants to heavy metals. In addition, it was demonstrated by pea seedling (Pisum sativum L.) growing experiments that CaAl-LDH/BC increased plant fresh weight, root length, plant height, catalase (CAT) activity, and protein content, which promoted the growth of the plant. Compared with BC, CaAl-LDH/BC significantly reduced the Cu and Pb contents in pea seedlings, in which the Cu and Pb contents in pea seedlings were reduced from 31.97 mg/kg and 74.40 mg/kg to 2.92 mg/kg and 6.67 mg/kg, respectively, after a 2% dosage of CaAl-LDH/BC, which was a reduction of 90.84% and 91.03%, respectively. In conclusion, compared with BC, CaAl-LDH/BC improved soil fertility and thus the plant growth environment, and also more effectively reduced the mobility of heavy metals Cu and Pb in the soil to reduce the enrichment of Cu and Pb by plants.
Keywords: CaAl-layered double hydroxides; heavy metal contamination; mining-contaminated soil; pea seedlings.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Super-stable mineralization of Cu, Cd, Zn and Pb by CaAl-layered double hydroxide: Performance, mechanism, and large-scale application in agriculture soil remediation.J Hazard Mater. 2023 Apr 5;447:130723. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.130723. Epub 2023 Jan 3. J Hazard Mater. 2023. PMID: 36640507
-
[Mn/Al-layered Double Oxide-loaded Biochar Reduced the Toxic Effects of Heavy Metals on Ryegrass in Soil].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2023 Feb 8;44(2):975-983. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202202219. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2023. PMID: 36775620 Chinese.
-
Phosphorus-modified biochar cross-linked Mg-Al layered double-hydroxide stabilizer reduced U and Pb uptake by Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) in uranium contaminated soil.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022 Apr 1;234:113363. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113363. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022. PMID: 35248924
-
Application of layered double hydroxide-biochar composites in wastewater treatment: Recent trends, modification strategies, and outlook.J Hazard Mater. 2021 Oct 15;420:126569. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126569. Epub 2021 Jul 3. J Hazard Mater. 2021. PMID: 34280719 Review.
-
Quantification of the effect of biochar application on heavy metals in paddy systems: Impact, mechanisms and future prospects.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Feb 20;912:168874. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168874. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38029988 Review.
References
-
- Baran H.A., Nalbantcilar M.T., Koktan N. Pollution and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Waters around Mine Sites of Elazig (Eastern Turkey) J. Mt. Sci. 2023;20:1293–1306. doi: 10.1007/s11629-022-7618-9. - DOI
-
- Mandal J., Bakare W.A., Rahman M.M., Rahman M.A., Siddique A.B., Oku E., Wood M.D., Hutchinson S.M., Mondal D. Varietal Differences Influence Arsenic and Lead Contamination of Rice Grown in Mining Impacted Agricultural Fields of Zamfara State, Nigeria. Chemosphere. 2022;305:135339. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135339. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

