Impact of Insertion Speed, Depth, and Robotic Assistance on Cochlear Implant Insertion Forces and Intracochlear Pressure: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 38894099
- PMCID: PMC11174543
- DOI: 10.3390/s24113307
Impact of Insertion Speed, Depth, and Robotic Assistance on Cochlear Implant Insertion Forces and Intracochlear Pressure: A Scoping Review
Abstract
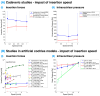
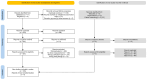
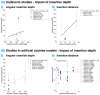
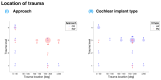
Cochlear implants are crucial for addressing severe-to-profound hearing loss, with the success of the procedure requiring careful electrode placement. This scoping review synthesizes the findings from 125 studies examining the factors influencing insertion forces (IFs) and intracochlear pressure (IP), which are crucial for optimizing implantation techniques and enhancing patient outcomes. The review highlights the impact of variables, including insertion depth, speed, and the use of robotic assistance on IFs and IP. Results indicate that higher insertion speeds generally increase IFs and IP in artificial models, a pattern not consistently observed in cadaveric studies due to variations in methodology and sample size. The study also explores the observed minimal impact of robotic assistance on reducing IFs compared to manual methods. Importantly, this review underscores the need for a standardized approach in cochlear implant research to address inconsistencies and improve clinical practices aimed at preserving hearing during implantation.
Keywords: angular depth; cochlear implantation; cochlear trauma; electrode design; hearing preservation; insertion approach; insertion depth; insertion forces; insertion speed; intracochlear pressure; robotic assistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

