Implementation of Engagement Detection for Human-Robot Interaction in Complex Environments
- PMID: 38894102
- PMCID: PMC11174507
- DOI: 10.3390/s24113311
Implementation of Engagement Detection for Human-Robot Interaction in Complex Environments
Abstract
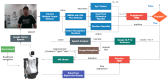
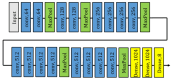
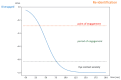
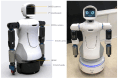
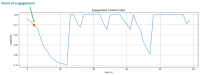
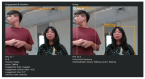
This study develops a comprehensive robotic system, termed the robot cognitive system, for complex environments, integrating three models: the engagement model, the intention model, and the human-robot interaction (HRI) model. The system aims to enhance the naturalness and comfort of HRI by enabling robots to detect human behaviors, intentions, and emotions accurately. A novel dual-arm-hand mobile robot, Mobi, was designed to demonstrate the system's efficacy. The engagement model utilizes eye gaze, head pose, and action recognition to determine the suitable moment for interaction initiation, addressing potential eye contact anxiety. The intention model employs sentiment analysis and emotion classification to infer the interactor's intentions. The HRI model, integrated with Google Dialogflow, facilitates appropriate robot responses based on user feedback. The system's performance was validated in a retail environment scenario, demonstrating its potential to improve the user experience in HRIs.
Keywords: action recognition; cognitive system; engagement; human behaviors; human–robot interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Group Emotion Detection Based on Social Robot Perception.Sensors (Basel). 2022 May 14;22(10):3749. doi: 10.3390/s22103749. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35632160 Free PMC article.
-
CARE: towards customized assistive robot-based education.Front Robot AI. 2025 Feb 21;12:1474741. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2025.1474741. eCollection 2025. Front Robot AI. 2025. PMID: 40061441 Free PMC article.
-
Gait-to-Gait Emotional Human-Robot Interaction Utilizing Trajectories-Aware and Skeleton-Graph-Aware Spatial-Temporal Transformer.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jan 25;25(3):734. doi: 10.3390/s25030734. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39943373 Free PMC article.
-
On human-in-the-loop optimization of human-robot interaction.Nature. 2024 Sep;633(8031):779-788. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07697-2. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Nature. 2024. PMID: 39322732 Review.
-
A Meta-Analysis on Remote HRI and In-Person HRI: What Is a Socially Assistive Robot to Do?Sensors (Basel). 2022 Sep 21;22(19):7155. doi: 10.3390/s22197155. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36236261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LLM-based robot personality simulation and cognitive system.Sci Rep. 2025 May 16;15(1):16993. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01528-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40379754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fraboni F., Brendel H., Pietrantonib L., Vidoni R., Dallasega P., Gualtieri L. Updating Design Guidelines for Cognitive Ergonomics in Human-Centred Collaborative Robotics Applications: An Expert Survey. Appl. Ergon. 2024;117:104246. - PubMed
-
- Moriuchi E., Murdy S. The Role of Robots in the Service Industry: Factors Affecting Human-Robot Interactions. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2024;118:103682. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2023.103682. - DOI
-
- Abiodun Odesanmi G., Wang Q., Mai J. Skill Learning Framework for Human–Robot Interaction and Manipulation Tasks. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2023;79:102444. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2022.102444. - DOI
-
- Li C., Zheng P., Yin Y., Pang Y.M., Huo S. An AR-assisted Deep Reinforcement Learning-based approach towards mutual-cognitive safe human-robot interaction. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2023;80:102471. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2022.102471. - DOI
-
- Li S., Zheng P., Liu S., Wang Z., Wang X.V., Zheng L., Wang L. Proactive Human-Robot Collaboration: Mutual-Cognitive, Predictable, and Self-Organising Perspectives. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2023;81:102510. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2022.102510. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

