Deep Learning-Based Nystagmus Detection for BPPV Diagnosis
- PMID: 38894208
- PMCID: PMC11175138
- DOI: 10.3390/s24113417
Deep Learning-Based Nystagmus Detection for BPPV Diagnosis
Abstract
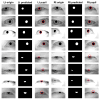
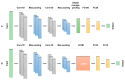
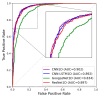
In this study, we propose a deep learning-based nystagmus detection algorithm using video oculography (VOG) data to diagnose benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). Various deep learning architectures were utilized to develop and evaluate nystagmus detection models. Among the four deep learning architectures used in this study, the CNN1D model proposed as a nystagmus detection model demonstrated the best performance, exhibiting a sensitivity of 94.06 ± 0.78%, specificity of 86.39 ± 1.31%, precision of 91.34 ± 0.84%, accuracy of 91.02 ± 0.66%, and an F1-score of 92.68 ± 0.55%. These results indicate the high accuracy and generalizability of the proposed nystagmus diagnosis algorithm. In conclusion, this study validates the practicality of deep learning in diagnosing BPPV and offers avenues for numerous potential applications of deep learning in the medical diagnostic sector. The findings of this research underscore its importance in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency in healthcare.
Keywords: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; convolutional neural network; horizontal nystagmus; nystagmus detection; pupil tracking.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Sung Ho Cho was employed by the company AMJ Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

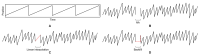
Similar articles
-
Transformer-Based Detection and Clinical Evaluation System for Torsional Nystagmus.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jun 28;25(13):4039. doi: 10.3390/s25134039. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648294 Free PMC article.
-
A nystagmus extraction system using artificial intelligence for video-nystagmography.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 24;13(1):11975. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39104-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37488184 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal deep learning-based diagnostic model for BPPV.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024 Mar 21;24(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12911-024-02438-x. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024. PMID: 38515156 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged Positional Downbeat Nystagmus in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Case Report and Literature Review.Am J Audiol. 2021 Jun 14;30(2):235-240. doi: 10.1044/2020_AJA-20-00187. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Am J Audiol. 2021. PMID: 33784182 Review.
-
Classification, diagnostic criteria and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017 Feb;44(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2016.03.013. Epub 2016 May 9. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017. PMID: 27174206 Review.
Cited by
-
Transformer-Based Detection and Clinical Evaluation System for Torsional Nystagmus.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jun 28;25(13):4039. doi: 10.3390/s25134039. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648294 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of Using Smartphone Eye Tracking for Self-Recording Positional Tests.Digit Biomark. 2025 May 23;9(1):98-103. doi: 10.1159/000545720. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Digit Biomark. 2025. PMID: 40535616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eggers S.D.Z., Bisdorff A., Von Brevern M., Zee D.S., Kim J.-S., Perez-Fernandez N., Welgampola M.S., Della Santina C.C., Newman-Toker D.E. Classification of Vestibular Signs and Examination Techniques: Nystagmus and Nystagmus-Like Movements. J. Vestib. Res. 2019;29:57–87. doi: 10.3233/VES-190658. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buttner U., Helmchen C., Brandt T. Diagnostic Criteria for Central Versus Peripheral Positioning Nystagmus and Vertigo: A Review. Acta Otolaryngol. 1999;119:1–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

