Cervical Spondylosis Diagnosis Based on Convolutional Neural Network with X-ray Images
- PMID: 38894217
- PMCID: PMC11174662
- DOI: 10.3390/s24113428
Cervical Spondylosis Diagnosis Based on Convolutional Neural Network with X-ray Images
Abstract
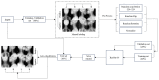
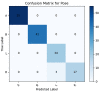
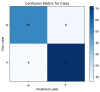
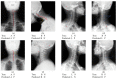
The increase in Cervical Spondylosis cases and the expansion of the affected demographic to younger patients have escalated the demand for X-ray screening. Challenges include variability in imaging technology, differences in equipment specifications, and the diverse experience levels of clinicians, which collectively hinder diagnostic accuracy. In response, a deep learning approach utilizing a ResNet-34 convolutional neural network has been developed. This model, trained on a comprehensive dataset of 1235 cervical spine X-ray images representing a wide range of projection angles, aims to mitigate these issues by providing a robust tool for diagnosis. Validation of the model was performed on an independent set of 136 X-ray images, also varied in projection angles, to ensure its efficacy across diverse clinical scenarios. The model achieved a classification accuracy of 89.7%, significantly outperforming the traditional manual diagnostic approach, which has an accuracy of 68.3%. This advancement demonstrates the viability of deep learning models to not only complement but enhance the diagnostic capabilities of clinicians in identifying Cervical Spondylosis, offering a promising avenue for improving diagnostic accuracy and efficiency in clinical settings.
Keywords: X-ray classification; cervical spondylosis; deep learning; multi-label.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Aided diagnosis of cervical spondylotic myelopathy using deep learning methods based on electroencephalography.Med Eng Phys. 2023 Nov;121:104069. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2023.104069. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Med Eng Phys. 2023. PMID: 37985026
-
AI-driven deep convolutional neural networks for chest X-ray pathology identification.J Xray Sci Technol. 2022;30(2):365-376. doi: 10.3233/XST-211082. J Xray Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35068415
-
Application of Imaging Examination Based on Deep Learning in the Diagnosis of Viral Senile Pneumonia.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 May 31;2022:6964283. doi: 10.1155/2022/6964283. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35694707 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning for report generation on chest X-ray images.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2024 Jan;111:102320. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2023.102320. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2024. PMID: 38134726 Review.
-
Recent developments in denoising medical images using deep learning: An overview of models, techniques, and challenges.Micron. 2024 May;180:103615. doi: 10.1016/j.micron.2024.103615. Epub 2024 Mar 2. Micron. 2024. PMID: 38471391 Review.
Cited by
-
DAEiS-Net: Deep Aggregation Network with Edge Information Supplement for Tunnel Water Stain Segmentation.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Aug 23;24(17):5452. doi: 10.3390/s24175452. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39275363 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-Based Machine Learning and Radiomics Methods for Assessing Spinal Cord Function in Patients with Mild Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Jun 17;12(6):666. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12060666. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564482 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

